
Innovation & Investment
Advances in breeding technologies for fish color traits in aquaculture
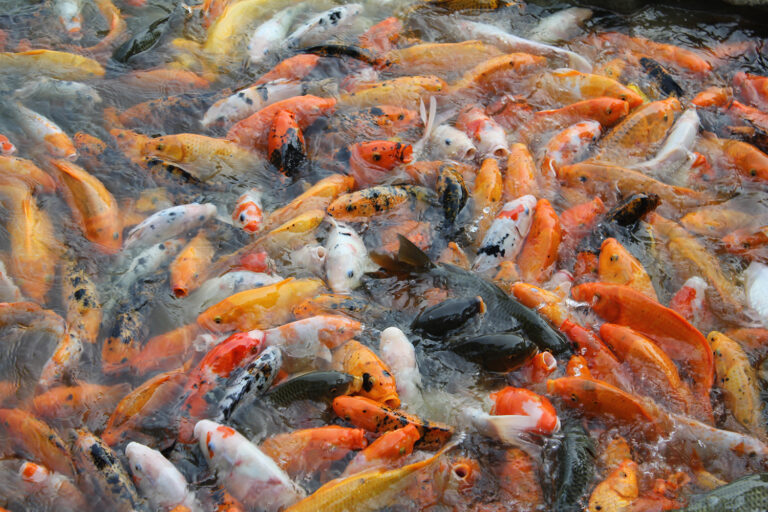
A review of the genetic and molecular mechanisms causing fish pigmentation provides framework for aquaculture genetic engineering strategies.
Intelligence
France Haliotis illustrates how determination can make the difference between survival and success in abalone aquaculture.

Innovation & Investment
A review of the genetic and molecular mechanisms causing fish pigmentation provides framework for aquaculture genetic engineering strategies.

Aquafeeds
Nofima researchers find that selective breeding yields faster-growing microalgae that produce more omega-3 fatty acids crucial to aquafeeds.

Intelligence
Seaweed farming experts are urging producers to employ selective breeding to capitalize on desired traits amid a changing climate.
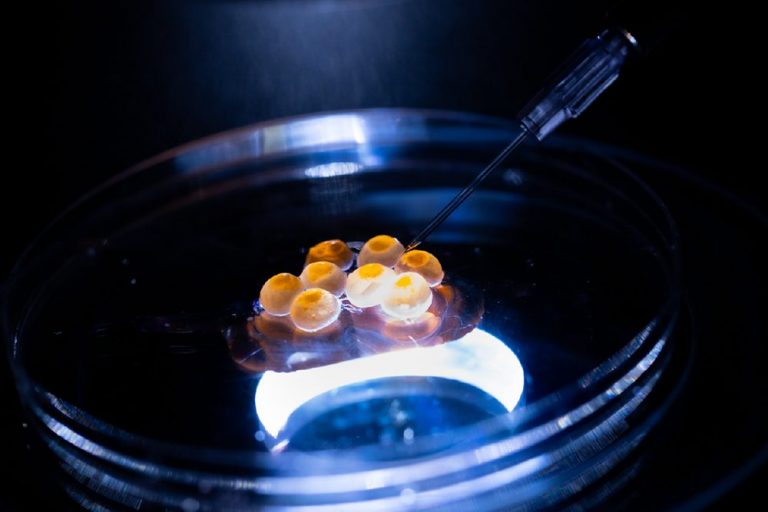
Innovation & Investment
Research in Japan shows genome editing can improve muscle growth in farmed fish, resulting in less feed and boosting disease resistance.
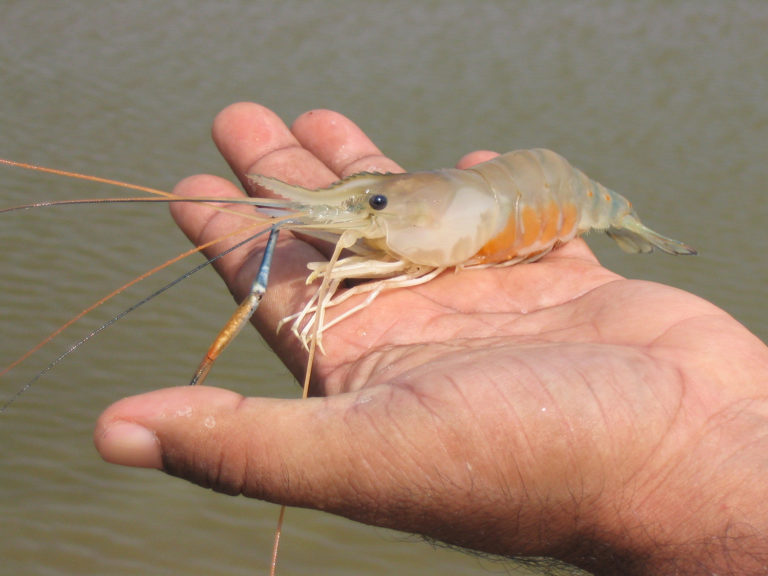

Health & Welfare
A selective breeding program for giant freshwater prawns in China provides valuable information for the breeding of the species.
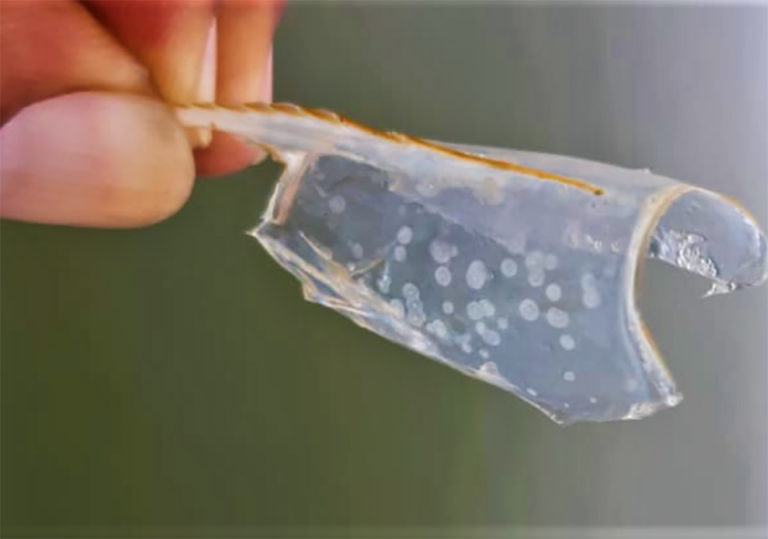

Health & Welfare
A study in Vietnam showed that there was significant variation in WSSV resistance among Pacific white shrimp families evaluated.
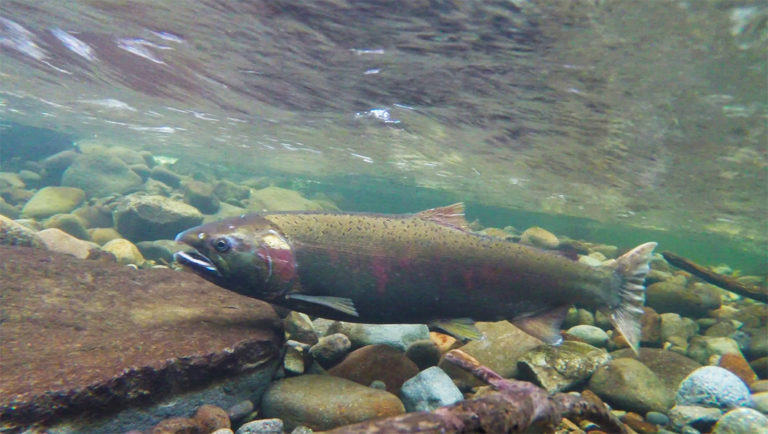

Health & Welfare
Genome editing can contribute to sustainable aquaculture production in terms of disease resistance and sterility to prevent interbreeding with wild stocks.

Health & Welfare
Due to high fecundity and external fertilization, most aquaculture species are amenable to genetic improvement technologies, including genome editing.
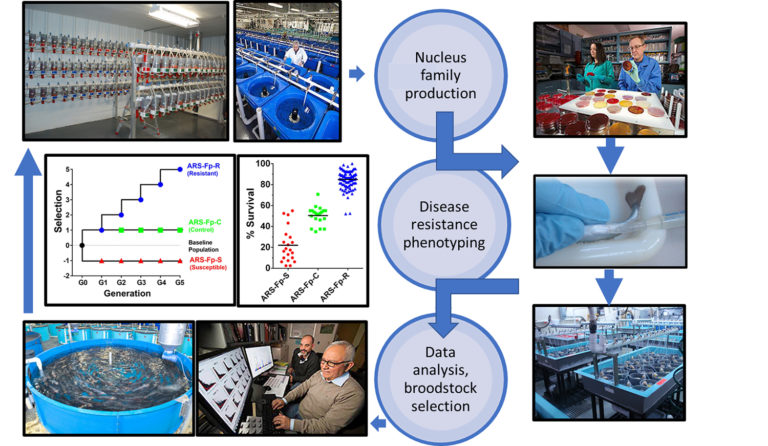
Health & Welfare
This study, involving more than 10 years of research on selective breeding, has shown that selective breeding can create considerable phenotypic divergence in rainbow trout lines when targeting a specific pathogen.
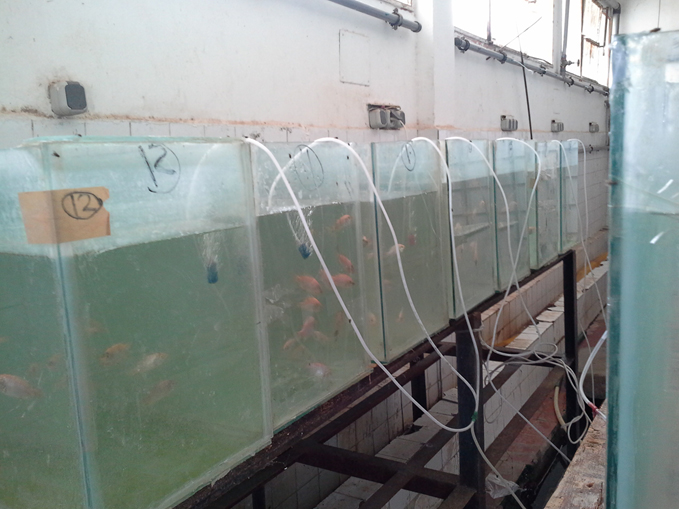

Health & Welfare
A major goal of selective breeding program for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Egypt is to select for fillet color and fillet weight in response to consumer preferences.
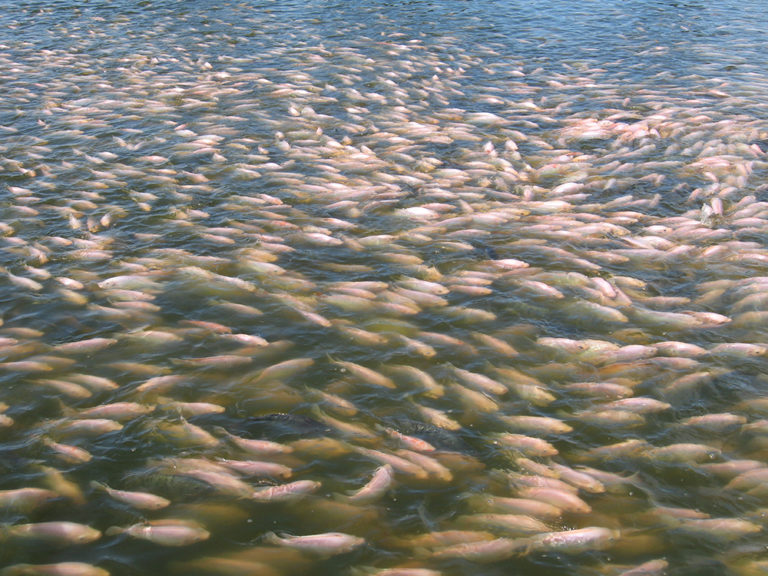

Intelligence
Tilapias are farmed in a variety of production systems, but mostly in freshwater and low-salinity waters. But tilapias are an excellent candidate for aquaculture in brackish- and seawater because they can tolerate a wide range of water salinity.
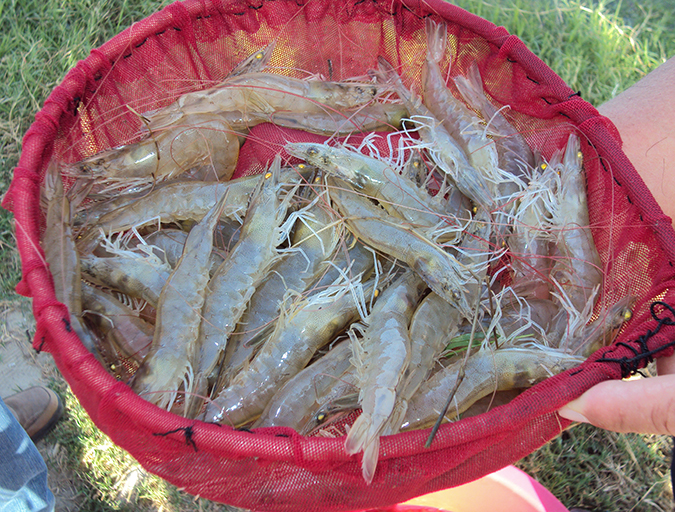

Health & Welfare
El alcanzar mayores tasas de crecimiento en el camarón cultivado comercialmente tiene muchos beneficios importantes, incluyendo la reducción de varios riesgos, la reducción de costos y el aumento de las oportunidades económicas. La genética del camarón determina principalmente cuanto crecimiento adicional se puede lograr, ya que el camarón típicamente refleja las tasas de crecimiento de sus progenitores.

Health & Welfare
Realizing higher growth rates in commercially cultured shrimp has many important benefits, including reducing various risks, cutting costs and increasing economic opportunities. Shrimp genetics primarily determines the amount of additional growth that can be achieved, as shrimp typically reflect their parents’ growth rates.
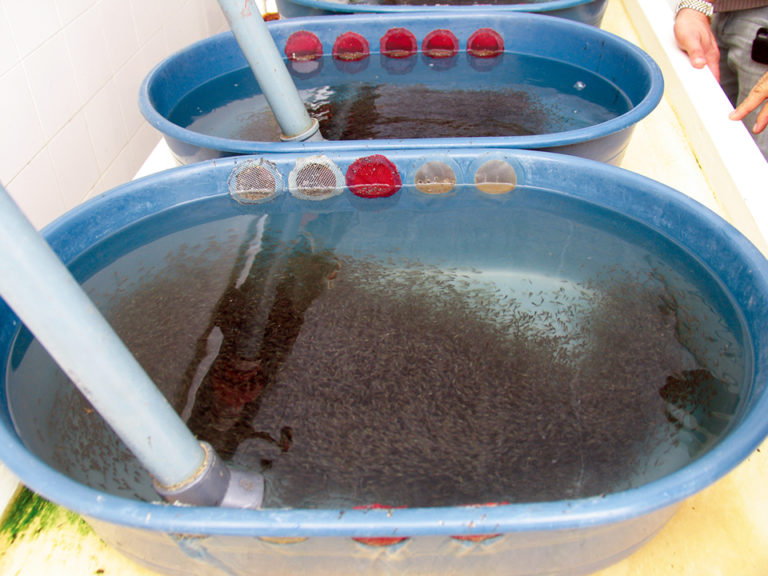

Health & Welfare
Although not universally practiced, the potential benefits of selective breeding in aquaculture outweigh all other options for improving animal performance. The genetic potential of aquaculture animals is plastic and can be improved over a relatively short timeframe.
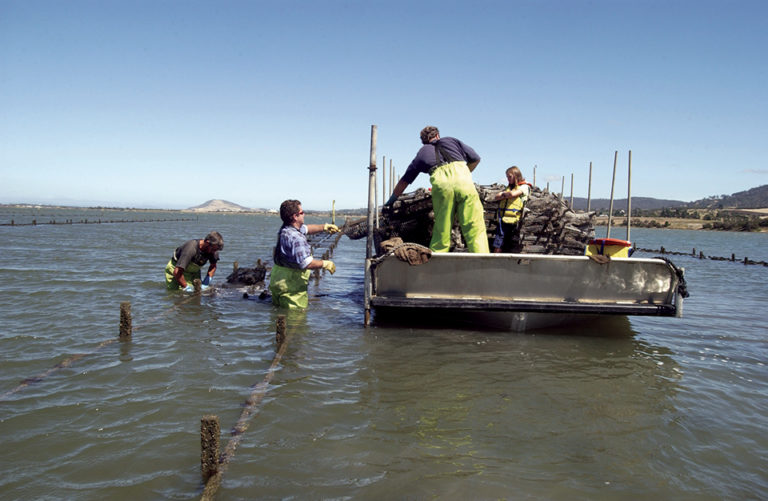

Health & Welfare
A partnership between CSIRO and the Australian seafood industry has significantly improved the selective breeding of Australian Pacific oysters.