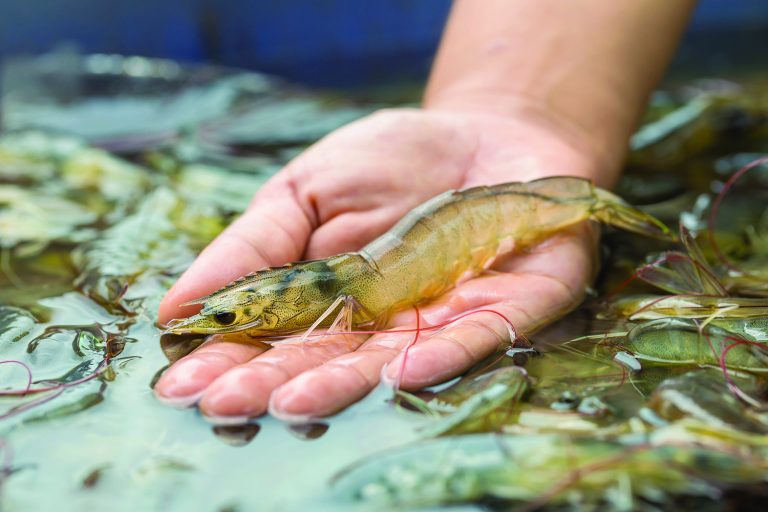

Aquafeeds
Evaluating hydrolysates as functional ingredients in Pacific white shrimp feeds
An evaluation of hydrolysates shows that cost-benefit, availability, quality and efficiency must be considered for feeding Pacific white shrimp.
Responsibility
In the latest GAIN article, fish scraps can be transformed into fish protein hydrolysates as a high-nutrient value addition to aquafeeds.

Aquafeeds
An evaluation of hydrolysates shows that cost-benefit, availability, quality and efficiency must be considered for feeding Pacific white shrimp.

Intelligence
Fish protein hydrolysates obtained from fish-processing wastes can be used to make valuable ingredients for the food and healthcare industries. Hydrolysates are produced from fish muscle and viscera through an autolytic process by endogenous enzymes or an accelerated method using exogenous enzymes.

Intelligence
Protein hydrolysates can be produced by acid, base or enzymatic hydrolysis processes. Acid hydrolysis produces salt that makes the product unsuitable for food and destroys some essential amino acids. An optimum process for one fish or shellfish by-product may not be optimum for another.
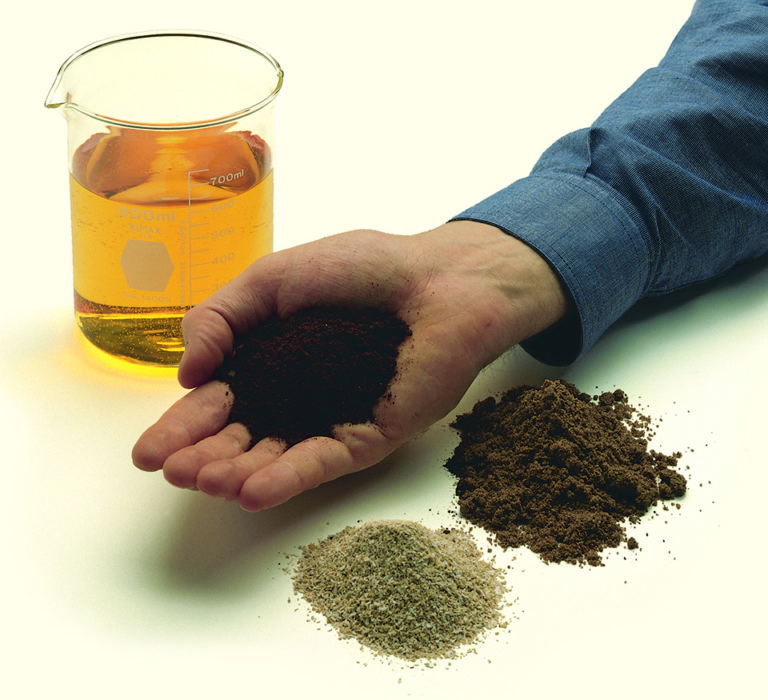

Aquafeeds
Key molecules found in animal byproduct hydrolysates show potential for use as functional ingredients in aquaculture feeds. Animal co-product hydrolysates from slaughterhouse waste and rendered animal byproducts present a protein alternative.
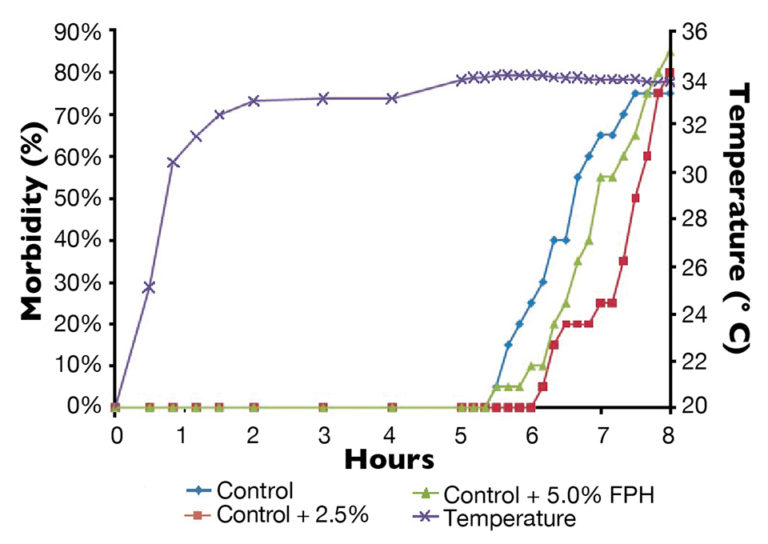
Health & Welfare
Fish protein hydrolysates are naturally rich in nutrients that can help support aquatic species’ immune defenses in resisting stressors.

Health & Welfare
Protein hydrolysates are currently used as partial substitutes for fishmeal in high-quality artificial diets since their inclusion in feeds promotes growth and survival.