
Responsibility
Phosphorus: Key to phytoplankton management
Phosphorus from uneaten feed and feces of culture animals can cause excessive phytoplankton growth and associated degradation of water quality.
Responsibility
Outside optimal salinity ranges, aquaculture species have higher feed-conversion ratios, grow at slower rates, become stressed and susceptible to disease, or even die.

Responsibility
Phosphorus from uneaten feed and feces of culture animals can cause excessive phytoplankton growth and associated degradation of water quality.

Responsibility
In the water of aquaculture systems, certain bacteria transform potentially toxic ammonia to nontoxic nitrate through nitrification.

Responsibility
Alkalinity is an index of the capacity of water to neutralize acidity. Hardness represents the sum of calcium and magnesium concentrations. Both values vary greatly in freshwater sources.
Responsibility
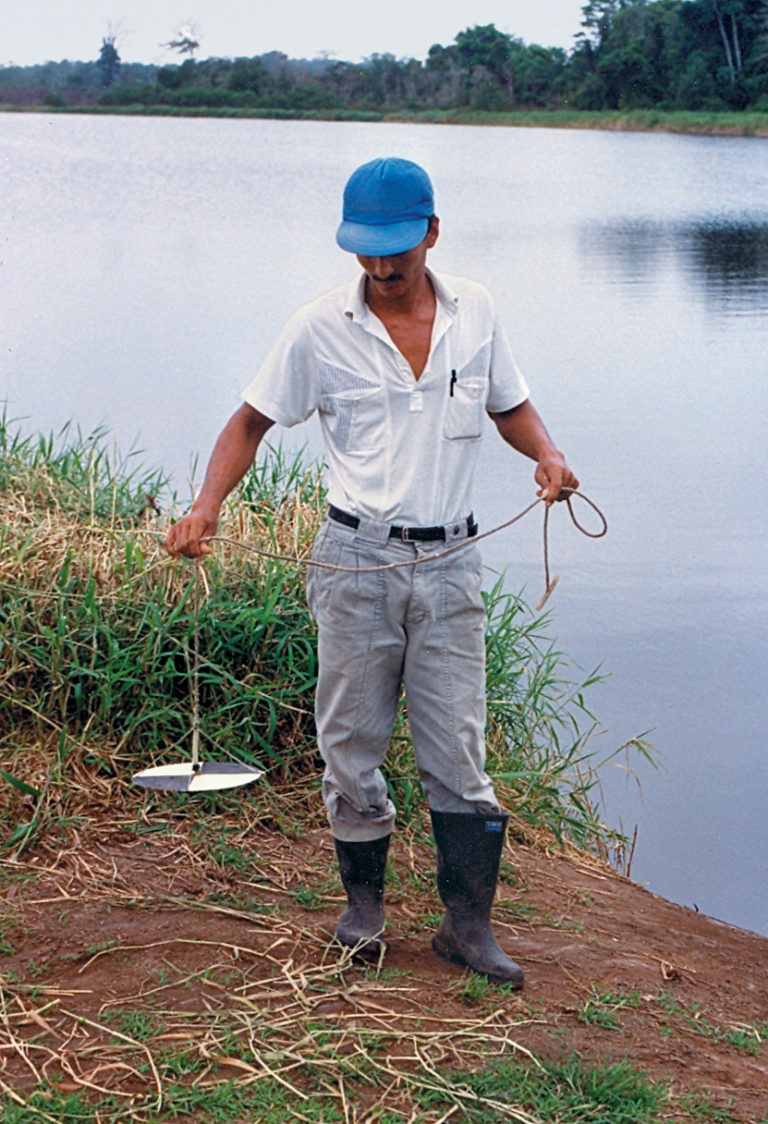
Simple tools can take water and sediment samples to monitor quality variables in aquaculture ponds. Water surface samples provide limited information, while water column sampling delivers more specific data.

Responsibility
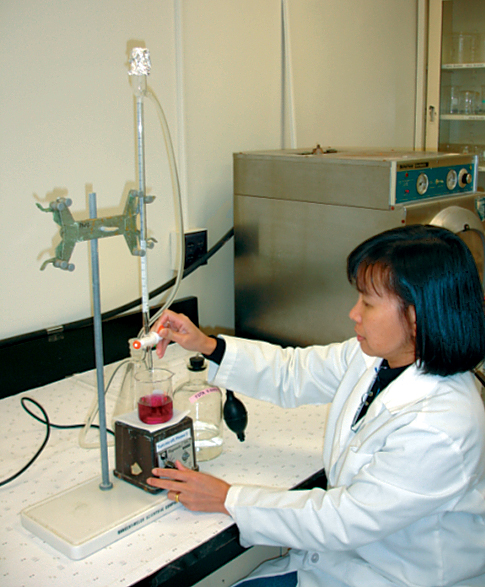
Although pond water samples collected to measure water quality are often held on ice, the values of some common variables in the samples can vary over time.

Responsibility
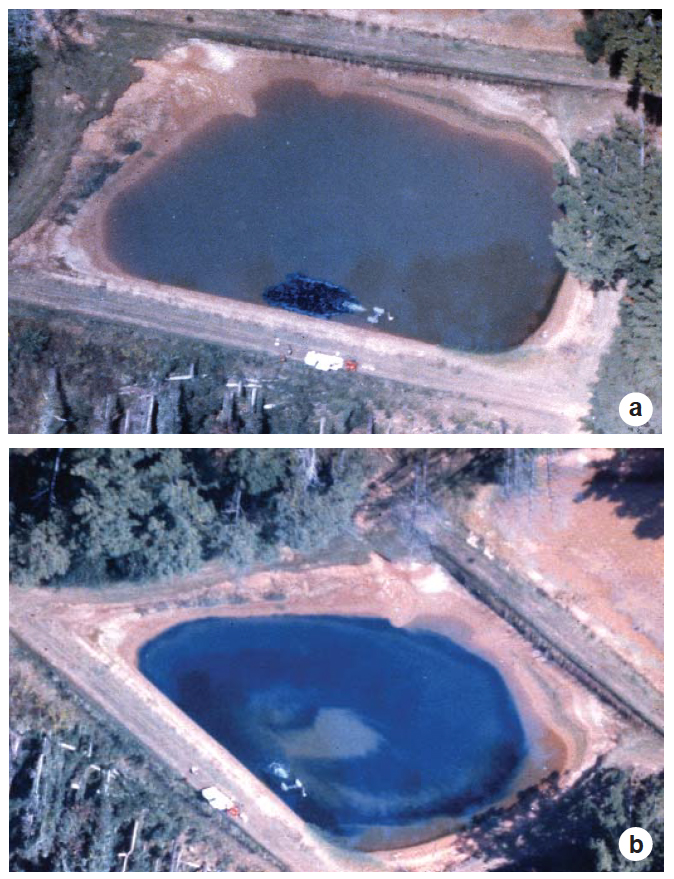
Phytoplankton are essential in intensive aquaculture ponds but an excess can result in shallow thermal stratification.

Responsibility
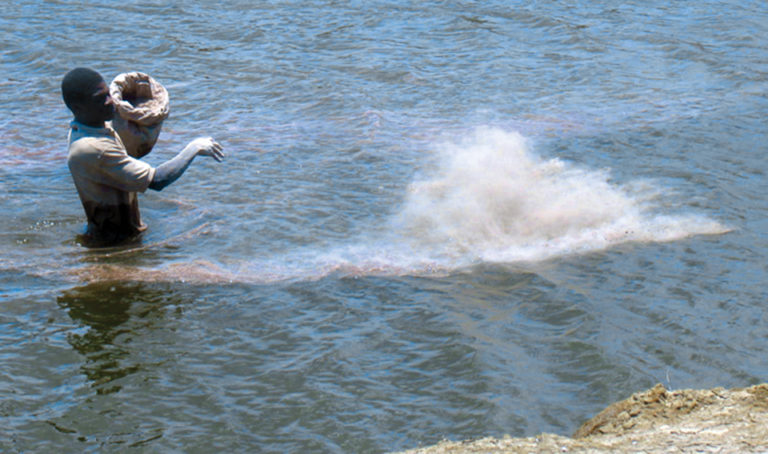
There are several methods for evaluating water circulation and mixing in aquaculture ponds. Measurements of concentrated salt dispersal can be complex.

Responsibility
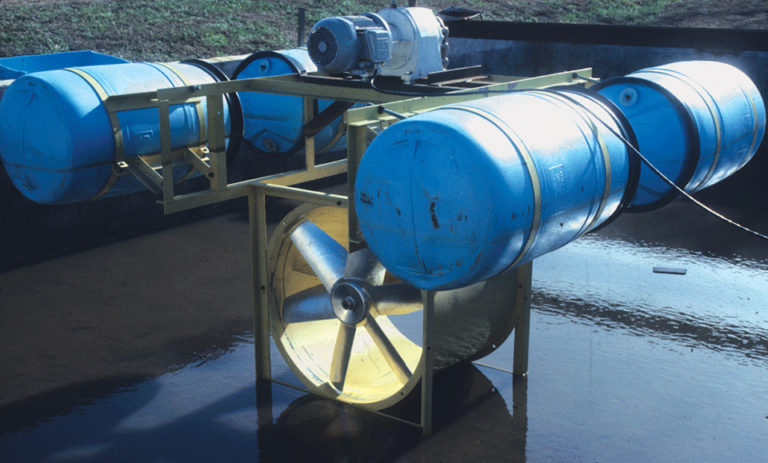
Mechanical water circulation can prevent stratification and provide more dissolved oxygen near pond bottoms. Strong water mixing can also control algae growth.

Responsibility
In general, lower-intensity pond and cage farming tends to discharge higher overall pollution loads in farm effluents than closed aquaculture systems.

Responsibility
Space requirements for aquaculture include the culture water area and associated physical culture facilities as well as the land used to raise plant-based feed ingredients.
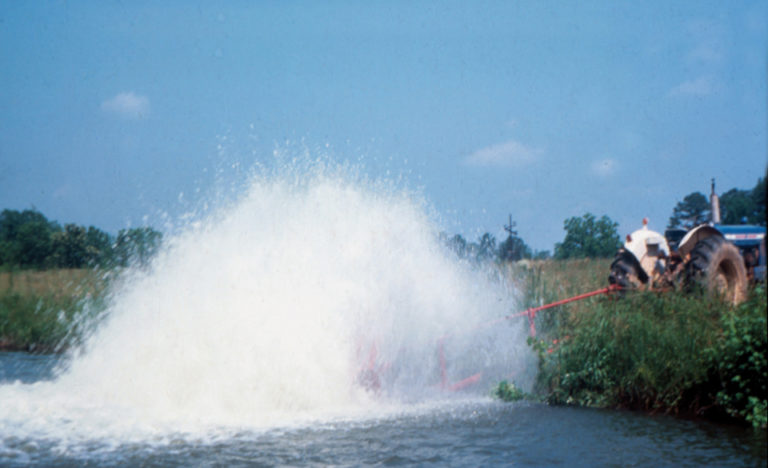

Responsibility
Even with dedicated aerators, aquaculture farms can experience stress and mortality in culture animals due to low dissolved oxygen concentrations in pond water. Simple tractor-powered aerators offer a quick and portable solution to low dissolved oxygen levels that provides strong emergency aeration and water movement.
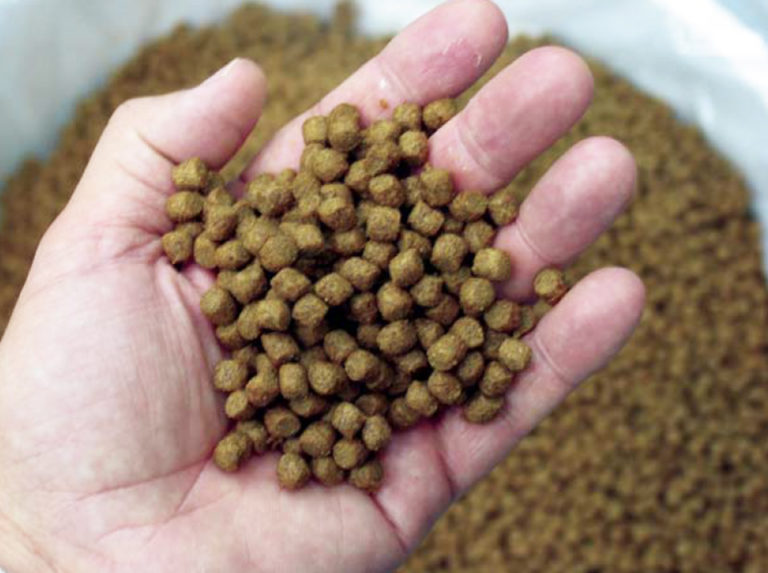

Aquafeeds
While feed conversion ratios are often used as indexes of feed efficiency, they can be misleading as ecological indicators.
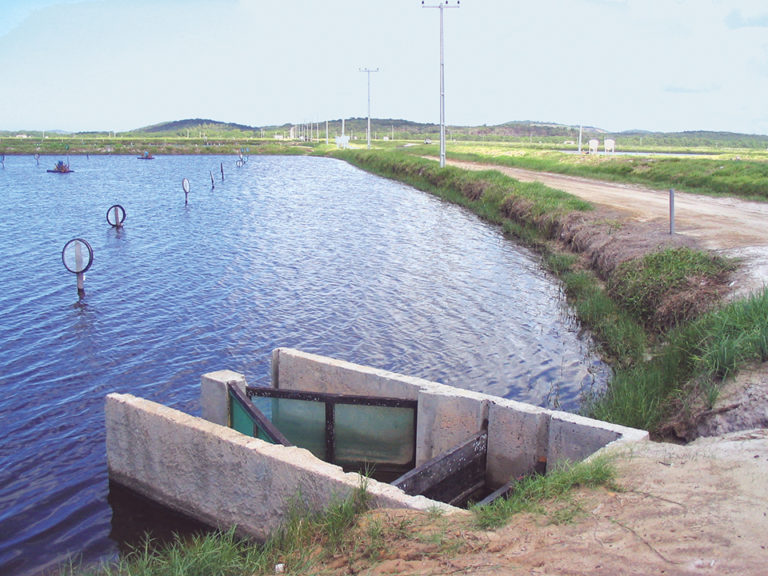

Responsibility
Water flow within channels can be measured using the float method or calculated using rating curves that project water velocity based on a series of finite measurements.
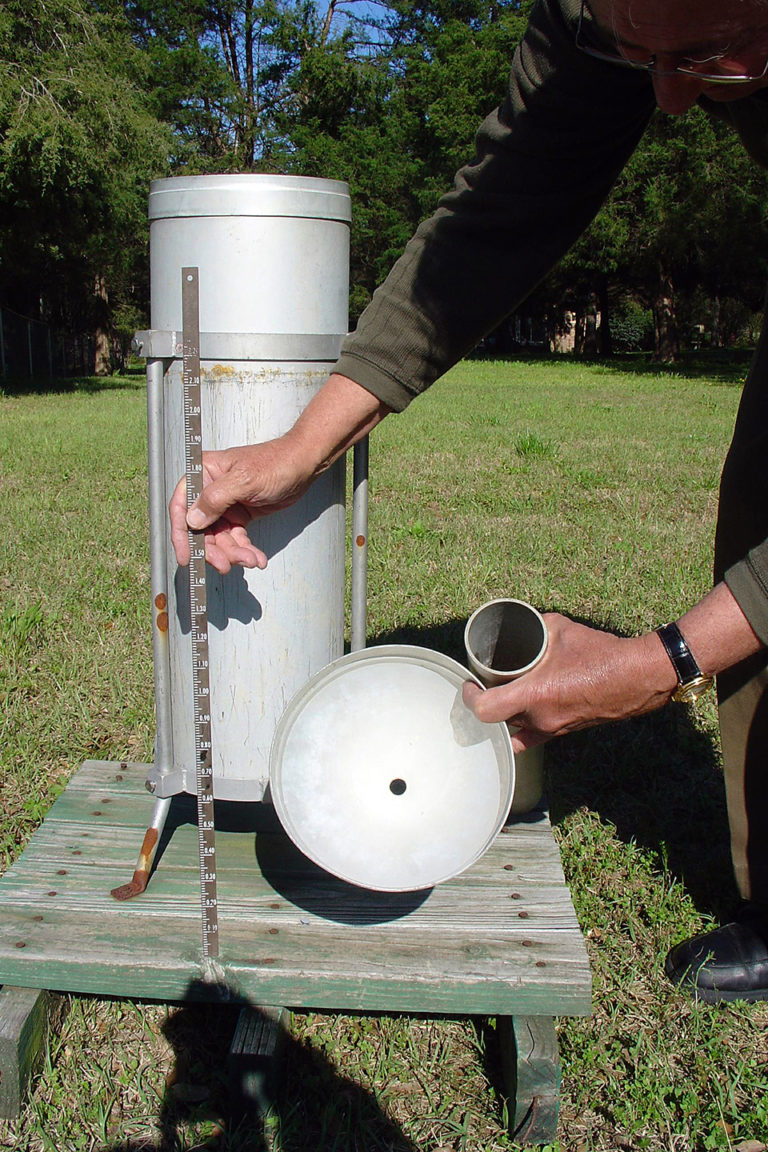

Responsibility
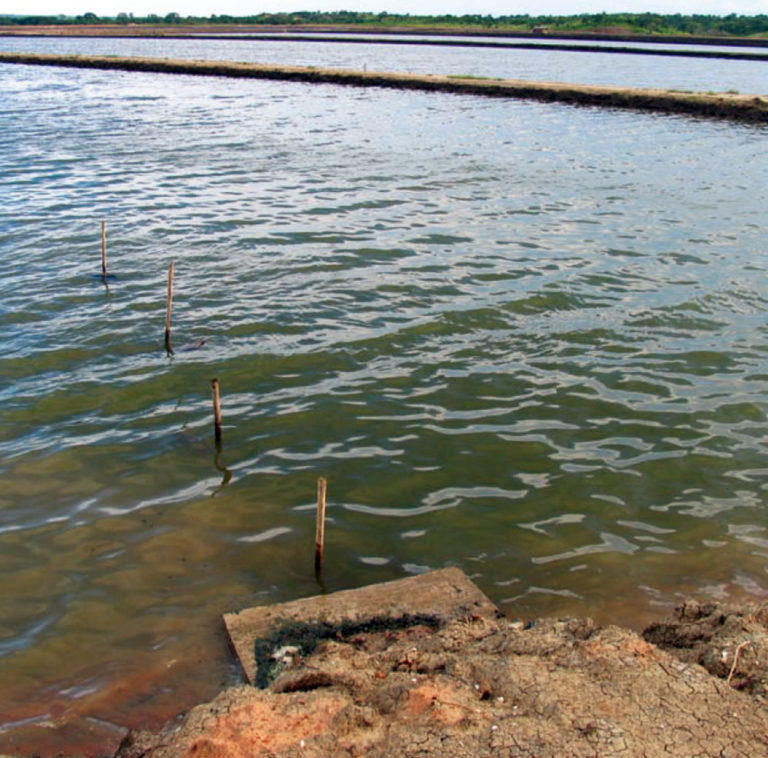
Accurate estimations of water volumes in aquaculture systems contribute to both better management of resources and cost-efficient production.
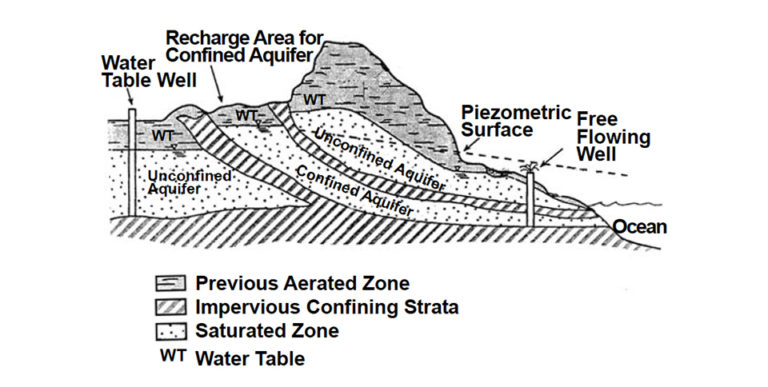
Responsibility
Groundwater from wells is sometimes used to supply hatcheries and ponds. The potential water supply via wells is defined largely by geology.