Trials evaluate levels of stress with various sediment parameters

The soil quality of production pond bottoms has long been recognized as a factor that influences pond water quality and aquatic animal production. Pond bottom conditions are particularly critical for shrimp, which spend most of their time on the bottom, burrow into the soil, and even ingest soil particles during feeding.
In general, uneaten feed, feces, plankton and debris settle in patterns throughout pond bottoms. This settling pattern can be affected by pond depth and water circulation. These factors introduce a high degree of spatial variability into soil parameters that is seldom considered in soil quality studies.
Osmotic pressure
Haemolymph osmotic pressure has been proposed as a parameter for the evaluation of the physiological state of penaeid shrimp, as it is influenced by a large variety of environmental parameters. It can be a convenient tool to detect areas of rearing ponds where sediments are degraded and potentially harmful to shrimp.
Field experiment
The authors’ recent study, conducted in an experimental semi-intensive shrimp pond in New Caledonia, evaluated the stress caused by sediment on shrimp held in bottom cages at different points of a pond and correlated the levels of stress with various sediment parameters.
Thirty shrimp with an average weight of about 13.2 grams were placed in 100- x 50- x 15-cm cages in 12 stations on the bottom of a 1-hectare pond. After 24 hours, samples of haemolymph from animals in intermolt stage were collected for osmotic pressure measurement.
The experiment was repeated four times. Each time, two groups of free-ranging shrimp of the same pond were sampled and used as controls. Simultaneously, sediment samples were collected and analyzed to evaluate some physicochemical parameters that could be related to the stress observed in the shrimp maintained in the cages.
The redox potential and pH of pore water of the first centimeter of pond bottom sediment were assessed in situ. Sediment samples of the top 1 cm were collected at each station and analyzed for water content, loss of weight, and total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) in the pore water.
Laboratory experiment
A laboratory test was carried out twice in six closed 70-liter tanks. Eight shrimp were placed in each tank for 24 hours. Five pH levels of 6.0 to 8.0 were tested. After a 24-hour exposure to different pH levels, shrimp haemolymph samples were collected for osmotic pressure measurements.
Results
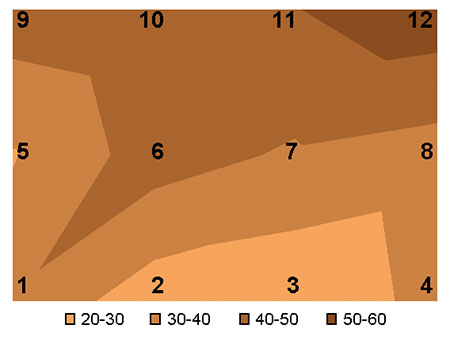
In seawater, an increase of osmotic pressure indicates a dysfunction in osmoregulation associated with various stressors. Fig. 1 is a schematic presentation of mean osmotic pressure in each cage in relation to the station. In some areas of the test pond, captive shrimp showed an increase of osmotic pressure.
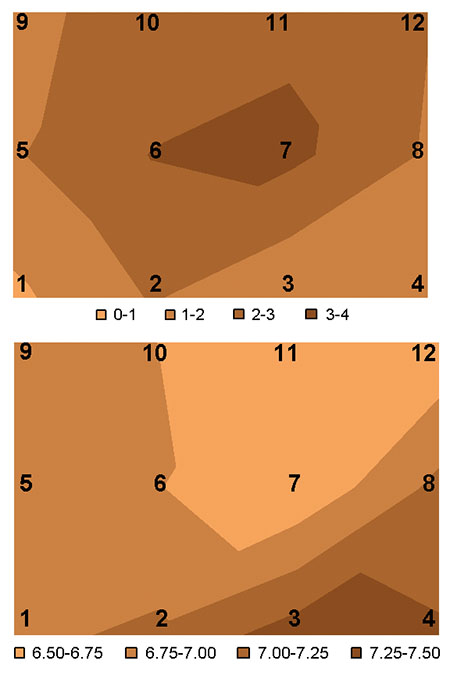
Fig. 2 is a schematic presentation of pond sediment parameters. The sediment loss of weight by combustion was most important in stations 1, 2 and 4, which were characterized by sediment with higher water content. TAN concentration was maximum in the center of the pond.
The lowest redox and highest pH values were found in stations 3 and 4, located in the deepest areas of the pond. The most significant correlation was between sediment pH and osmotic pressure of the captive shrimp.
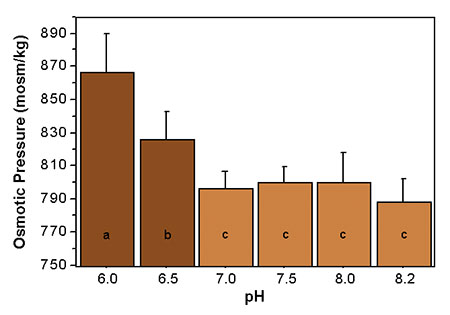
Post experiment laboratory analyses (Fig. 3) showed that low pH led to an increase of osmotic pressure. This increase seemed to be correlated to a pH range of 6.0 to 7.0, supporting the field test observations. Osmotic pressure of captive shrimp is directly related to the acidity of sediment.
Conclusion
Studies of shrimp held in cages on a pond bottom showed a spatial variability in the animals’ physiology related to the locations of the cages. The most significant correlation was between sediment pH and osmotic pressure of captive animals. Extreme values of pH are known stress factors for crustaceans, and postexperiment laboratory checks showed that low pH led to an osmotic pressure increase.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the October 2004 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Authors
-
-
Eric Bernard
IFREMER
B.P. 2059 98846 Nouméa
New Caledonia -
Eric Boglio
IFREMER
B.P. 2059 98846 Nouméa
New Caledonia -
Cyrille Goarant
IFREMER
B.P. 2059 98846 Nouméa
New Caledonia -
Jean-Claude Cochard
IFREMER
B.P. 2059 98846 Nouméa
New Caledonia
Tagged With
Related Posts

Responsibility
A look at various intensive shrimp farming systems in Asia
The impact of diseases led some Asian shrimp farming countries to develop biofloc and recirculation aquaculture system (RAS) production technologies. Treating incoming water for culture operations and wastewater treatment are biosecurity measures for disease prevention and control.

Health & Welfare
A study of Zoea-2 Syndrome in hatcheries in India, part 1
Indian shrimp hatcheries have experienced larval mortality in the zoea-2 stage, with molt deterioration and resulting in heavy mortality. Authors investigated the problem holistically.

Health & Welfare
A study of Zoea-2 Syndrome in hatcheries in India, part 2
Indian shrimp hatcheries have experienced larval mortality in the zoea-2 stage, with molt deterioration and resulting in heavy mortality. Authors considered biotic and abiotic factors. Part 2 describes results of their study.

Responsibility
Advancing shrimp farm technologies support greater efficiencies, sustainability
Todays' shrimp farm technologies include biosecurity protocols, stocking densities according to pond design and aeration levels, and best practices for pond preparation and feed and water management.


