The effort supports the conservation of horseshoe crabs, which are important to human medicine
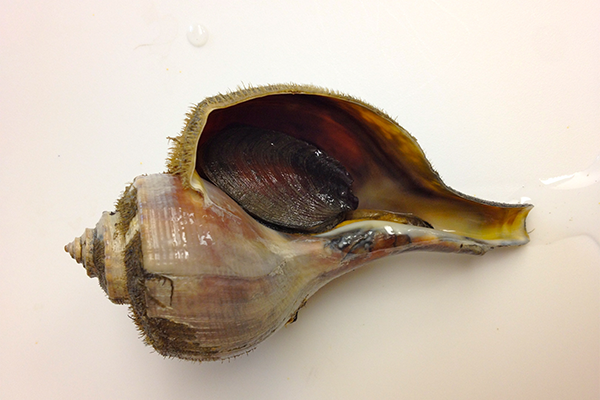
Researchers at the University of New Hampshire’s Coastal Marine Lab are finding ways to make whelk fishing more sustainable by designing smarter traps and by developing a bait that does not use horseshoe crabs, a declining species that’s become important to human medicine.
Fisheries for channeled whelk (Busycotypus canaliculatus) populations in the United States, along the Eastern Seaboard from Massachusetts down to Florida, are moving to stricter size and trap limits and some are closing temporarily. But the UNH team says modified whelk traps with escape vents can retain the greatest number of legal-sized whelks and let sublegal-sized whelks escape. It’s a solution that’s cost-effective for fishermen to do on their own.
“Some whelk fishermen already modify their traps with escape vents,” explained Elizabeth Fairchild, a research associate professor in the department of biological sciences. “The Massachusetts Division of Marine Fisheries wants to see an escape vent added, so it’s only a matter of time before they mandate the change and a configuration that fishermen will need to use.”
A team at the UNH Coastal Marine Lab in New Castle, N.H., has been testing modified whelk traps with escape vents and bait recipes that use little to no horseshoe crab for the past two years. This whelk fishing season, which is from April to December in Massachusetts, they have worked with local fishermen to determine if modified traps result in less sorting of sublegal whelk and if new bait recipes work as well as – or better than – the horseshoe crab bait.

With the modifications, they hope to bridge the gap between the fishermen and the resource management agencies to find an effective solution.
An alternative to horseshoe crab would help conserve a species that’s a key food source of migratory birds up and down the Eastern seaboard and a scientifically critical species used in the production of vaccines and other medicines due to the unique toxin-identifying quality of horseshoe crab’s blue-colored blood.
Whelk and eel fishermen have used horseshoe crab as a preferred bait source for years and an alternative will need to meet several criteria to become widely used.
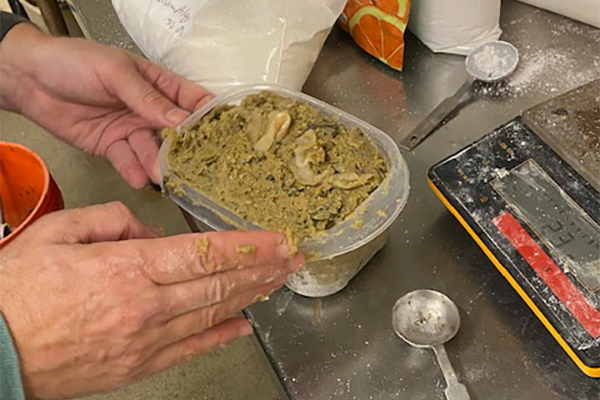
“Whelk fishermen all have unique recipes that they use for bait, however, the common denominator in all these is horseshoe crab, particularly female horseshoe crab,” said Fairchild. “So we need new bait recipes that can be made using no or low-cost materials, like seafood waste, that won’t cost more than what they are already using and – most importantly – that are as effective in attracting channeled whelk into the traps.”
Channeled whelk don’t normally eat horseshoe crab in the wild – they commonly predate on bivalves like oysters and clams – so it’s a bit of a mystery why it works so well as a bait source, they said. At the Coastal Marine Lab, the UNH team has tested dozens of recipes, trying different combinations of everything from poultry byproduct meal and clam processing byproduct to invasive green crabs and surf clams that wash up on the beaches.
“Once we came up with our winning recipe consisting of clam bellies and green crab – held together by a binder – we tested its preservation, how it could be stored frozen and then thawed for use,” added Fairchild. Local fishermen have trialed the bait this season.
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Author
Tagged With
Related Posts

Health & Welfare
Can farming horseshoe crabs help the COVID-19 cause?
Already housing horseshoe crabs for medical purposes, researchers hope recirculating aquaculture systems will aid their coronavirus-fighting efforts.

Responsibility
Aquaculture diversification in Chile: Potential of giant barnacles
Current work to support culture of giant barnacles illustrates the process of developing production technologies and their transference within Chile.

Intelligence
Assessing the use of gamma-irradiated chitosan from mangrove horseshoe crabs on refrigerated seafood products
An effective chitosan polymer, developed through gamma-irradiation, could preserve seafood and extend shelf-life beyond capabilities of refrigeration.
Health & Welfare
Economic impacts of aquatic parasites on global finfish production
Obligate and opportunistic parasites play a critical role in determining the productivity, sustainability and economic viability of global finfish aquaculture enterprises. Without stringent and appropriate control measures, the impacts of these pathogens can often be significant.



