First discovered in Brazil in 2002
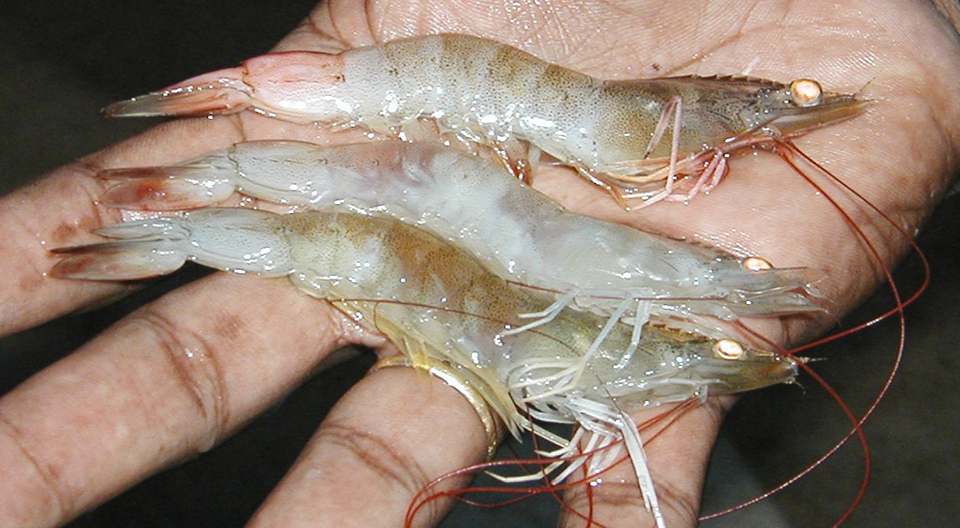

Infectious myonecrosis (IMN) was recently identified in cultured Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in northeastern Brazil. IMN presents as a disease with an acute onset of gross signs and elevated mortalities, but progresses with a chronic course accompanied by persistent low-level mortalities.
The disease was first recognized by shrimp farmers as a distinctive phenomenon in September 2002 at a shrimp farm in Pernambuco in the state of Piaui. The infectious nature of IMN was experimentally demonstrated in 2003, with the causative agent identified as a new virus.
To date, IMN appears to be limited to northeastern Brazil. However, shrimp with similar gross signs have also been reported in other countries where L. vannamei are cultured.
Mortalities
IMN affects postlarvae, juveniles, and subadult pond-reared stocks of L. vannamei. Losses due to IMN in 2003 were estimated at approximately U.S. $20 million by Nunes and coauthors in the May/June 2004 Panorama da Aqüicultura. Outbreaks of the disease seem to be associated with environmental and physical stresses such as extremes in salinity and temperature, collection by cast net, and possibly the use of low-quality feeds.
Clinical signs and histopathology
Affected shrimp present focal to extensive white necrotic areas in striated muscles, especially the distal abdominal segments and tail fan, which can become necrotic and reddened in some individual shrimp. Since the progression of the disease is relatively slow, but with persistent mortalities, feed-conversion rates tend to increase and add to economic losses.
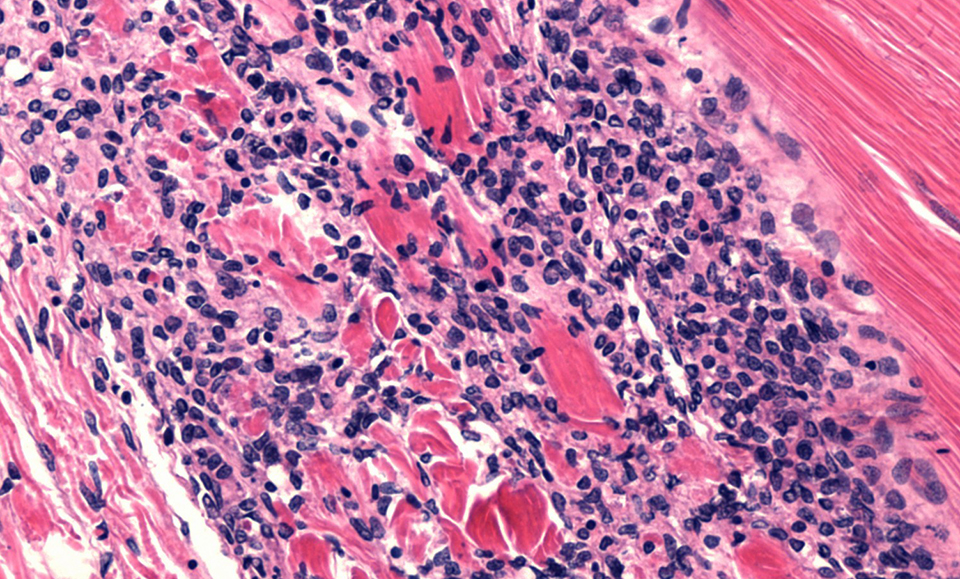
By histopathology, shrimp with acute-phase IMN present lesions with coagulative muscle necrosis, often with edema. In shrimp recovering from acute IMN or those in its more chronic phase, the necrosis appears to progress from coagulative to liquefactive. This progression is accompanied by hemocytic infiltration and fibrosis (Fig. 1).
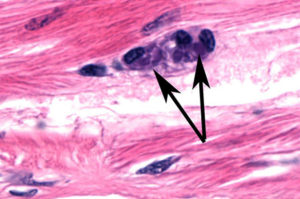
Significant spheroid formation is typically present in the lymphoid organ, and ectopic lymphoid organ spheroids are often found in the hemocoel and loose connective tissues, especially in the heart lumen and adjacent to antennal gland tubules. In some histological preparations, perinuclear pale to darkly basophilic inclusion bodies are evident in muscle cells (Fig. 2), connective tissue cells, hemocytes, and cells that comprise lymphoid organ spheroids.
Identification, diagnostic methods
A 40-nm-diameter spherical virus has been isolated from naturally infected shrimp with the disease. The virus has been partially characterized, and portions of its nucleic acid (RNA) genome have been cloned and sequenced.
Molecular probes and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) methods for IMN diagnosis have been developed and will be reported. A commercial RT-PCR kit for IMN will likely be on the market in late 2004 or early 2005.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the October 2004 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Authors
-

D.V. Lightner, Ph.D.
University of Arizona
Aquaculture Pathology Group
Tucson, Arizona 85721 USA -
C.R. Pantoja, Ph.D.
University of Arizona
Aquaculture Pathology Group
Tucson, Arizona 85721 USA -
B.T. Poulos
University of Arizona
Aquaculture Pathology Group
Tucson, Arizona 85721 USA -
K.F.J. Tang
University of Arizona
Aquaculture Pathology Group
Tucson, Arizona 85721 USA -
R.M. Redman
University of Arizona
Aquaculture Pathology Group
Tucson, Arizona 85721 USA -
T. Pasos-de-Andrade
University of Arizona
Aquaculture Pathology Group
Tucson, Arizona 85721 USA -
J.R. Bonami
University of Arizona
Aquaculture Pathology Group
Tucson, Arizona 85721 USA
Tagged With
Related Posts

Responsibility
A look at various intensive shrimp farming systems in Asia
The impact of diseases led some Asian shrimp farming countries to develop biofloc and recirculation aquaculture system (RAS) production technologies. Treating incoming water for culture operations and wastewater treatment are biosecurity measures for disease prevention and control.

Health & Welfare
A study of Zoea-2 Syndrome in hatcheries in India, part 1
Indian shrimp hatcheries have experienced larval mortality in the zoea-2 stage, with molt deterioration and resulting in heavy mortality. Authors investigated the problem holistically.

Health & Welfare
Biofloc technology: Possible prevention for shrimp diseases
Facing emerging viral problems and rising energy costs, the use of biofloc technology in biosecure systems offers an answer for sustainable shrimp aquaculture. The main attributes of biofloc systems in reducing disease risk include the fact that low water exchange improves pathogen exclusion.

Health & Welfare
Biosecurity principles for sustainable production using SPF shrimp
Basic components of biosecurity include knowledge of diseases, adequate detection methods and the use of “clean” shrimp stocks.


