Trials to focus on better understanding fish parasite’s possible routes of infection
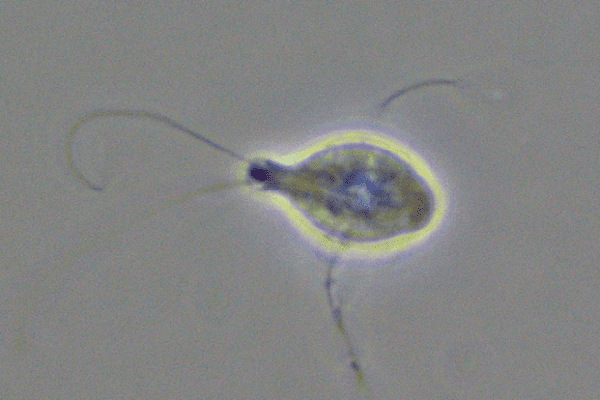
A new research project is seeking to better understand Spironucleus salmonicida, a small parasite that is “causing concern” for salmon farms in Northern Norway.
Spironucleosis can kill fish but also negatively impact the fish quality, resulting in large quantities being discarded upon slaughter. To prevent the spread of the parasite, it’s often necessary to slaughter all infected fish populations, which makes the parasite a major threat to the aquaculture industry.
In 2022, the parasite and the disease were detected in several fish farms in Northern Norway, and the parasite was also detected for the first time in a smolt production facility. There has also been an increase in the number of infected fish, as well as a possible spread between neighboring net pens at sea.
“The aim of the SpiroFri project is to gain increased knowledge about the parasite so that the industry can prevent the pathogen from entering and spreading in smolt production facilities, and therefore, prevent it from appearing in farmed fish that have been transferred to the sea,” said Bjørn Olav Kvamme, project manager and research director at the Institute of Marine Research (IMR).
The SpiroFri project has received NOK 7 million (approximately U.S. $667,000) in support from the Norwegian Seafood Research Fund, with a total budget of NOK 8.9 million (approximately $848,000). It is a collaborative project between the Institute of Marine Research, Nofima, the Norwegian Veterinary Institute, Pure Salmon Kaldnes and Grieg Seafood.
The project will involve a review of current findings and data on the parasite; investigations of biosecurity measures and consequences of infection in hatcheries; and trials that investigate possible routes of infection among the fish.
“The special thing about this parasite is that it leaves the intestine where it typically resides and enters the bloodstream,” said Egil Karlsbakk, research scientist and scientific responsible at the IMR. “No one knows why and how it penetrates the intestinal wall. When it enters the bloodstream, it can spread to all parts of the fish, which is why we say the infection is systemic. It can enter the brain and form abscesses in the internal organs and the muscle.”
Salmon, sea trout, Arctic sea char and lumpfish will all be part of the research project. A pilot infection trial led by food research institute Nofima has already been carried out with salmon in seawater at the Aquaculture Research Station in Tromsø.
At IMR, marine scientists will investigate the role these fish species play in the spread of infection, and if infection from fish farming facilities can have a detrimental effect on those species as well.
“It turns out that lumpfish used as cleaner fish in the net pens have been infected, which is new information – such as the fact that the parasite can also infect fish that are not salmonids,” said Karlsbakk. “We are therefore concerned that it can also spread to other species. Our trials are currently focused on how to infect the fish.”
The research team expects to have a first report as early as this summer. The findings should help prevent the spread of infection and deal with problems and losses caused by the parasite.
“The parasite has been detected in wild salmonids living in freshwater that is used as a water source for hatcheries, which therefore represents a potential source of infection that we must try to control,” said Lill-Heidi Johansen, scientist and project manager at Nofima.
Read more about the SpiroFri project.
Follow the Advocate on Twitter @GSA_Advocate
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Author
Tagged With
Related Posts

Health & Welfare
Microbiome of parasite can impact salmon health, scientists say
The microbiome of a parasite – meaning everything that lives inside the parasites – can play a role in salmon health, a new study says.

Intelligence
Could floating cages revitalize an oyster farming industry decimated by the MSX parasite?
Study says floating cages could help revitalize the Cape Breton oyster farming industry destroyed by MSX parasite 20 years earlier.
Health & Welfare
No fluke: Cawthron Institute’s new web tool could help fish farmers tackle parasitic infection
Cawthron Institute has developed “BeNeZe” – a new web tool to help fish farmers manage parasitic infection in Kingfish and Amberjacks

Health & Welfare
Gene editing eyed as a potential sea lice solution
A Nofima-led study is exploring the possibilities of using gene editing to make salmon more resistant to sea lice.



