
Sequencing batch reactors effectively treat shrimp aquaculture wastewater
One simple method of treating high-nitrogen wastewater in shrimp aquaculture is the use of sequencing batch reactors, which are simple in design.
Evaporation of water from ponds is influenced by solar radiation, air and water temperature, and wind velocity. Control of aquatic plants can yield some reduction.

One simple method of treating high-nitrogen wastewater in shrimp aquaculture is the use of sequencing batch reactors, which are simple in design.

To design a settling basin, know the size distribution of particles, estimated rate of inflow and determination of the smallest particle size to be removed.

A practical way to treat mariculture effluents combines the physical attributes of a sand filter and the biological properties of hungry marine sand worms.

Aquaponic systems are robust, management is not difficult, and the synergies between fish and plants make vegetable production more profitable than aquaculture alone. The lion’s share of marine agriculture involves salt-tolerant halophytic plants used as food or feed, or in energy production.

Those interested in using groundwater for aquaculture should perform a thorough chemical analysis of the water. Several problems related to groundwater use in hatcheries and holding or transport vessels can be alleviated by degassing or aeration.

Proper site selection, consideration of soil properties and careful earthwork construction at shrimp farms are essential. Prevention of erosion protects farm infrastructure and reduces sediment accumulation in ponds.

Common factors that affect water chiller performance are inadequate water flow, inadequate heat recovery, inappropriate compressors and imbalances among compressor, condenser, evaporator and thermal expansion valves.

The wide distribution and ongoing improvement of GIFT tilapia in Sri Lanka is raising living standards and employment for women in rural areas.

The inadequate supply of postlarvae is a bottleneck for prawn production in Bangladesh. A shortage of wild broodstock to supply the hatcheries is an ongoing concern.

U.S. policies are intended to facilitate sustainable marine aquaculture, restore natural resources and enhance fisheries. Additional initiatives address shellfish production, aquaculture management in the Gulf of Mexico and technology transfer.
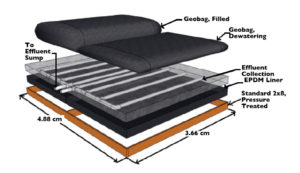
One promising new technology for dewatering aquaculture solid waste is the use of geotextile bags: porous, sealed tubular containers constructed of high-strength, woven polyethylene material.

In modifying its infrastructure and related pond management, QVD Aquaculture uses floating water plants to remove nitrogen and phosphorus from the discharge water. Sludge pens capture sludge at ponds for later reuse.

Seaweed farming has both proven history and huge potential. Large-scale farms could produce raw materials for biofuel, aquatic feeds and human consumption.
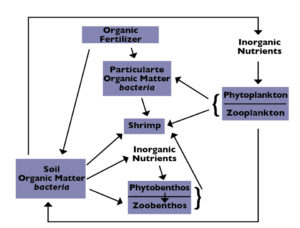
Animal manures, grasses and other organic matter have been widely used as fertilizers in aquaculture ponds. The fertilizers decompose and release nutrients that promote the growth of phytoplankton and enhance the base of the food web.

Spiny lobsters are a premium seafood whose culture has depended on wild-caught seedstock. An Australian company is helping shift the farming paradigm to more sustainable hatchery production.