
Necrotizing hepatopancreatitis: Diagnosis, distribution in shrimp
Necrotizing hepatopancreatitis has become one of the most important bacterial diseases affecting shrimp farming in the Americas.
At a United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) workshop 14 shrimp-producing countries discussed strategies for controlling shrimp diseases.

Necrotizing hepatopancreatitis has become one of the most important bacterial diseases affecting shrimp farming in the Americas.

A 14-day study evaluated mortalities related to TSV exposure, as broodstock resistant to an “old” strain succumbed to a “new” Belize strain of the virus.

Yellow perch is an emerging aquaculture candidate susceptible to a wide range of disease syndromes with infectious and non-infectious causes.

Shrimp virus detection requires innovative options in tools for viral diseases, such as polymerase chain reaction and isothermal nucleic acid amplification.

The authors ran a series of three trials to test the effects of increased water temperature on the survival rates of juvenile TSV-exposed shrimp.

From planting seed to monitoring the environment, shellfish farmers have to manage their crops wisely to rear healthy animals and run profitable operations.

High-pressure processing can destroy or inactivate microbial cells in seafood to improve shelf life, quality and food safety.
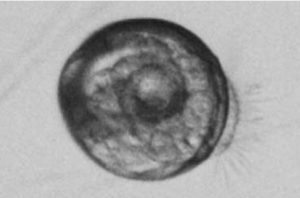
At oyster hatcheries around the world, prevention and control of infectious bacterial diseases has involved the use antibiotics and disinfectants.

In Mexico, there is interest in the culture of various finfish species, including bullseye puffers, a commercially important fish with aquaculture potential.

The authors evaluated the effects of a yucca extract on water quality and the production parameters of Pacific white shrimp.
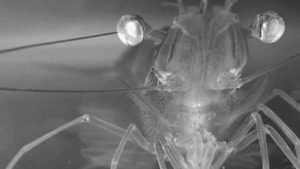
To understand shrimp feeding behavior, the Oceanic Institute investigated feed delivery systems and responses to experimental diets.
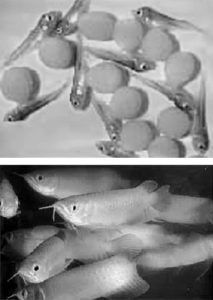
Microsatellites are useful for molecular tagging of individuals and molecular dissection of complex traits such as growth, temperature tolerance and disease resistance.
In a recent effort to produce specific pathogen-free (SPF) stocks of the fleshy prawn, researchers from two U.S. institutions collaborated.

The aim of functional genomics on innate antiviral immunity in marine shrimp is to characterize the genes involved in the response to WSSV and other viruses.

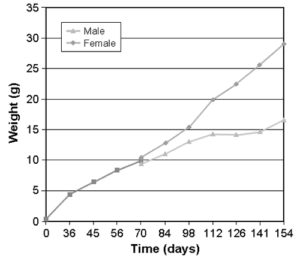
With the fleshy prawn (Fenneropenaeus chinensis), family selection appears to be a promising prospect that could enhance WSSV resistance.