
Starvation timing affects morphology, growth of first-feeding halibut larvae
The authors recently evaluated the physical deterioration of first-feeding California halibut larvae using morphometric and histological criteria.
Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institution researchers have developed marine fish culture methods on an experimental to pilot scale.

The authors recently evaluated the physical deterioration of first-feeding California halibut larvae using morphometric and histological criteria.

Domestication and genetic improvement of the Kuruma prawn (Penaeus japonicus) have been relatively slow due to availability of broodstock and postlarvae.

Proper nutrition is crucial to maintain growth and health in farmed fish. A variety of dietary factors and nutritional strategies can be influential.
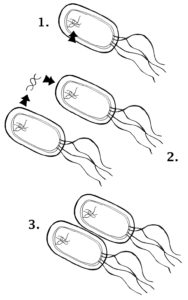
When an antibiotic is administered, the usual effective dose may be insufficient to control an infection if the invasive microorganism has developed resistance.

The cumulative effects of shrimp hatchery harvest, packing, temperature change, transporting and acclimation have an impact on postlarvae survival.

In an experiment in which tilapia were sorted by size and reared separately, large individuals maintained their size advantage after eight weeks of culture.

Asian sea bass (Lates calcarifer) feeding strategies and diets must be developed for slow-growth (winter) and fast-growth (summer) seasons.

Intensively cultured Paracalanid copepods represent a valuable new diet for rearing small tropical marine fish larvae under biosecure conditions.

Do fish grow differently because of variations in growth efficiency or social hierarchies that affect the feeding behavior in tanks or cages?

The dramatic transformation of the shrimp sector in Asia was fueled by the switch from monodon shrimp to P. vannamei seedstock from Hawaii.

Often forming large colonies, cyanobacteria – aquatic, photosynthetic organisms – represent one of the largest and most important bacteria groups.

A shrimp diet developed in trials is the first dry nursery diet shown to ensure good performance at stocking densities up to 45,000 per square meter.
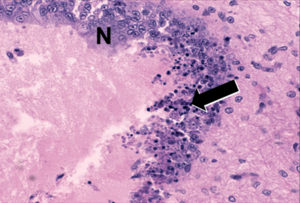
Shrimp farming in Belize, Central America, was hard hit by Taura Syndrome Virus (TSV, now known as TSV serotype A) in 1996 and a re-emergence in 2002.

FDA’s regulatory definition for trans-fatty acids is all unsaturated fatty acids that contain one or more isolated double bonds in a trans configuration.

Both microsatellite and AFLP marker analyses can provide adequate screening of genetic diversity in tilapia stocks at a low cost.