
Controlled cooking methods offer higher shrimp yields with product safety
Advances in equipment design keep pace to provide uniform, controlled cooking temperatures that allow more precise bacteria lethality with higher yields.
The black spots of melanosis quickly arise in harvested shrimp from enzymatic reactions in shrimp tissue or external stressors.

Advances in equipment design keep pace to provide uniform, controlled cooking temperatures that allow more precise bacteria lethality with higher yields.

The Central Pertiwi Bahari farms in Indonesia found polyculture of white shrimp and black tiger shrimp at a density of 70 PLs per square meter promising.

In a study, microbial flocs contributed about 50 percent of feed material as dry solids and about 50 percent of the protein requirement of tilapia.

Southern flounder offer potential in aquaculture to answer declining fishery landings and increased demand, but insufficient fingerlings are available.

A recent study showed the sensitivity of Sydney rock oyster embryos to small amounts of disinfectants and other substances commonly used in hatcheries.

New antibody-based diagnostic kits for aquaculture disease diagnosis are simple and fast, and high-sensitivity PCR testing is coming to the field, as well.
The successful development of efficient tank culture techniques for sunshine bass fry and fingerlings would help in the year-round production of fish of uniform size and quality.

Artificial diets are used to replace live artemia at commercial shrimp hatcheries, but complete replacement remains a challenge for strong grow-out results.

Seaweed products like extracts are ingredients in many beauty products and creams, and widely marketed as natural herbal and weight-reduction products.

Tiger flatworms hold promise as a source for ecteinascidins, a class of antitumor compounds under study for human cancer treatment.

Penaeid shrimp need the same nutrients required by all animals, including protein, lipids, energy sources, vitamins, minerals, oxygen and water.
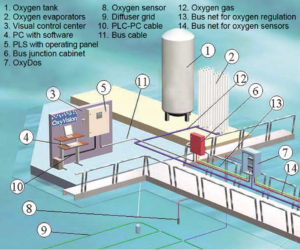
A commercial oxygen injection system tested in Norway maintained D.O. at levels that sustained growth and increased the harvested biomass.

The Quality Index Method provides guidelines for objectively assessing seafood freshness with specific criteria for individual species.

While freezing, salting, smoking and irradiation can minimize growth biogenic amine formation, special care from harvest through consumption can prevent scombrotoxin poisoning.

Since biogenic amines are a health issue in seafood, harvesters and processors should understand what conditions encourage their formation, where they form in fish, and how they are affected by bacterial flora.