
Feed deprivation reduces resistance of juvenile channel catfish to ESC
Witholding feed from channel catfish during the manifestation of enteric septicemia is a common practice, but discontinued feeding after an ESC challenge increased mortality.
Preliminary results indicate that rainfall events and animal feed lots contribute to increasing the amount of fecal contamination in bivalve mollusks.

Witholding feed from channel catfish during the manifestation of enteric septicemia is a common practice, but discontinued feeding after an ESC challenge increased mortality.

South African abalone culture is growing and many of the land-based tank production systems use wild-harvested kelp to feed the animals.

A model shrimp breeding program in Mexico used a large data set to estimate the heritability of body weight in different environments and the mean family breeding value for body weight using BLUP methodology.

Determining changes in the genetic diversity of selected hatchery stocks provides a means to monitor inbreeding, control loss of genetic diversity and achieve sustainable levels of genetic gain.

The Hubbs-SeaWorld Research Institute’s Mission Bay Laboratory has had limited success hatching and rearing eggs from captive wild yellowtail jack broodstock, but its program is improving.

Although the hatchery rearing of bivalves currently relies heavily on the mass production of microalgae, new feed alternatives are being developed.

Studies indicate that feeding channel catfish once daily to satiation from advanced fingerlings to market size provided maximum growth and production.

In studies, high dissolved carbon dioxide concentrations in culture tank water induced rainbow trout to swim to an area with lower concentrations.

In studies that compared performance of channel catfish hatcheries, eggs hatched six hours sooner with lower-oxygen incubation, but experienced lower survival.
In channel catfish diets, amino acid uptake from purified feed supplements is faster than from intact proteins in practical feed ingredients.

Microbial flocs consist of a variety of bacteria, fungi, microalgae and other organisms suspended with detritus in culture water.

The excellent culture characteristics of hybrid walking catfish have made them the dominant culture type in Thailand.

Decisions on stocking channel catfish fry should be based on the abundance of large zooplankton in the pond water, rather than total zooplankton abundance.

In trials with two commercial aquafeeds, juvenile cobia exhibited excellent growth and feed conversion. Higher-than-required lipid levels in the diets did not improve growth.
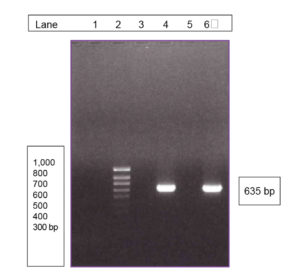
Probiotics are naturally occurring microbes in cultured animals or their environments that compete with bacterial pathogens to favorably alter the rearing environment and improve animal health. The success of a probiotic strain depends not only upon its stated and actual performance, but also its safety to the target organism, humans, and the surrounding environment.