Nutrition and genes research at Virginia Tech
Transcriptomics studies highlight impacts of different treatments on specific genes that can be targeted via nutritional intervention to increase farmed animal performance or welfare.
In periphyton-based aquaculture, the various invertebrates that colonize the hard substrates provided in ponds supplement artificial feed.

Transcriptomics studies highlight impacts of different treatments on specific genes that can be targeted via nutritional intervention to increase farmed animal performance or welfare.

A Brazilian study demonstrated it is cost-competitive to grow Chitralada tilapia up to 1 kg in small cages via intensive culture.

Research at YSFRI’s new Genetic and Breeding Center for Mariculture in Qingdao, China, has produced 180 full-sib and half-sib lines of fleshy shrimp.

Policies to limit antibiotic use spurred interest in alternative strategies, such as dietary supplementation with immunostimulants and other compounds.

Fish oil replacements in feeds alter the nutritional profiles of farmed fish. The challenge is to determine how and when to feed plant or fish oils to maintain desirable omega-3 levels in fillets.

The addition of methyltestosterone to freshwater prawns diets did not significantly change the percentage of males in the population, but reduced survival.

In a technology transfer, a semi-abandoned hatchery for black tiger shrimp in Indonesia was remade with applied hatchery methods refined in the West with white shrimp.

Vitamin E is a required element in tilapia diets influenced by dietary lipid levels. A 5 percent lipid diet is sufficient to maintain immune responses and healthy reproduction.

In trials, finishing diets improved the appearance of sea bass and sea bream with equivalent or higher performance than that achieved with standard grow-out diets.

A study developed a rapid, nondestructive and sensitive method to evaluate the condition of farmed Atlantic salmon using mass spectrometry with protein chip technology.

Inadequate levels of omega-3s in Senegal sole larvae diets can result in retarded growth, delayed metamorphosis, pigmentation problems and high mortalities.

Advances in genomics assist aquaculture science by deepening the understanding of adaptation, physiology and quantitative genetics.
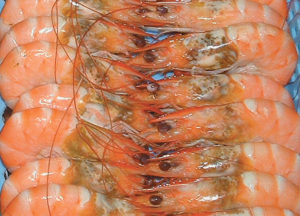
A shrimp's ruptured or discolored hepatopancreas is from a combination of factors involving nutrition, stress or toxins at various production chain levels.

Genetics is an important factor in shrimp farming. Improvements in disease resistance and robustness can be achieved with within-family selection, shorter generation intervals and marker-assisted selection.

A super-intensive RAS grow-out trial produced 5.7 kg of shrimp per square meter in 14 weeks using minimal water volume and only 0.34 percent daily water exchange.