
Self-recruiting species diversify polyculture systems
Even in commercial systems, management of self-recruiting species within diverse polycultures can reduce risk and produce valuable byproducts.
A revitalization of the huge integrated Dipasena Citra Darmaja farm complex is directing individual farmers to raise white shrimp using biosecure protocols in a modular culture approach.

Even in commercial systems, management of self-recruiting species within diverse polycultures can reduce risk and produce valuable byproducts.

A USDA/ARS program is studying semen cryopreservation with rainbow trout to insure that genetic diversity from multiple populations and the genetic legacy of selectively bred populations are protected.

Results from two studies at Oceanic Institute indicated that shrimp behavior may compromise growth at super-intensive stocking densities.
The release of cultured red king crab juveniles into the ocean presents a possible way to enhance stocks. Research in Russia found that early crab postlarvae did not feed, but swim actively.

Trials indicated that in order to determine methionine and TSAA requirements for shrimp, methionine must be added to research feeds in either a chelated or covalently bound form.
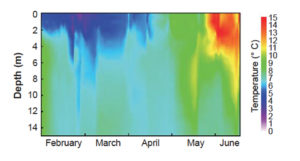
Since the early 1990s, salmon farmers have added lights to their cages from midwinter to midsummer to reduce the incidence of sexual maturation and improve fish growth.

The USDA marine aquaculture center is addressing genetic improvement of North American Atlantic salmon to develop improved lines for producers.

Regulations on antibiotics in aquaculture vary by country and region, from outright bans to minimal oversight.

Since physical and chemical hazards in seafood remain largely unchanged in storage, shelf life can be based on the growth kinetics of microbial hazards.

To overcome Infectious Myonecrosis Virus-related mortalities in cultured white shrimp, some Brazilian shrimp farmers tested the southern brown shrimp in grow-out ponds.

The principle of vaccination is based on two key elements of immunity: specificity and memory. Shrimp lack the appropriate cells and pathways to respond to specific pathogens and the long-term “memory” to deal with recurring infections.

Although its final quality can be variable, fish silage can be an effective protein supplement in feeds for various fish, shellfish and terrestrial animals.

In periphyton-based aquaculture, the various invertebrates that colonize the hard substrates provided in ponds supplement artificial feed.
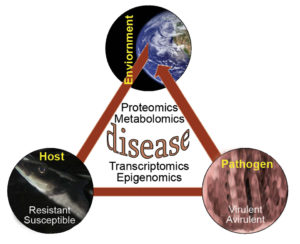
Transcriptomics studies highlight impacts of different treatments on specific genes that can be targeted via nutritional intervention to increase farmed animal performance or welfare.

A Brazilian study demonstrated it is cost-competitive to grow Chitralada tilapia up to 1 kg in small cages via intensive culture.