
Clay particles an alternative water treatment in marine fish larvae tanks
Clay particles present an alternative to water treatments with microalgae or algae paste in the culture water of marine fish larvae.
Research indicates that rendered protein meals could replace significant amounts of fishmeal in diets for shrimp and several cultured fish species without reducing weight gain.

Clay particles present an alternative to water treatments with microalgae or algae paste in the culture water of marine fish larvae.

Virginia Tech Aquaculture Research Group collaborated with MariCal to examine commercial feasibility of raising cobia in RAS under low-salinity conditions.

Hubbs-SeaWorld Research Institute and Universidad Autónoma de Baja California are working to produce improved broodstock diets for white sea bass and totoaba.
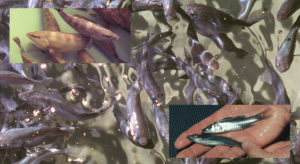
Stocking marine fish in coastal impoundments in Florida, USA, has demonstrated improved habitat quality and given hatchery fish a transition to open water.

The development of specific pathogen-free Pacific white shrimp and breeding led to rapid adoption of the domesticated shrimp throughout the Western Hemisphere and Asia.

Breeding efforts at Aquatec Genearch Aquacultura in Brazil have centered on specific pathogen-free white shrimp lines imported from the United States.

The Atlantic Cod Genomics and Broodstock Development Project has expanded the gene-related resources for the species in Canada.

Experiences with newly domesticated shrimp species in Australia underscore the importance of understanding the species' biological requirements.

Resistant to antibacterial agents and heat, biofilms are difficult to remove from food-processing surfaces and may result in persistent pathogen populations.

As Fiji considers a change in culture species from blue to black tiger shrimp, a study evaluated viruses in the country’s wild P. monodon stocks.
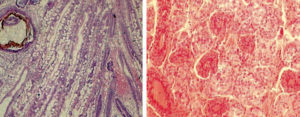
Loose Shell Syndrome is a slow killer of black tiger shrimp in India. Affected shrimp exhibit mortality and reduced survival rates and production.

Tilapia vaccines can protect the fish against infectious diseases by providing pathogen-specific acquired immunity that prevents recurring infections.

Dietary nucleotide supplementation represents a potential means to enhance aquaculture efficiency and profitability, but gaps in current knowledge exist.

About 60 percent of China’s aquaculture production is freshwater fish. Carps top the list, although many other native and non-native species are also raised.

A new scalable modular concept for lobster culture developed in Norway relies on automation to perform most production procedures.