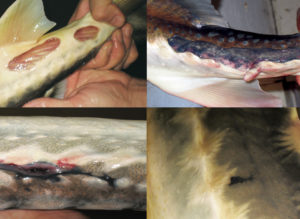
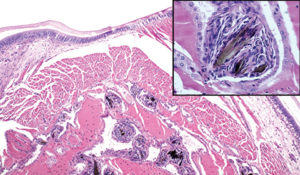
Selective breed high-efficiency seedstock boost integrated shrimp farm performance
The foundation of a successful integrated aquaculture company is reliable production of healthy postlarvae. Methodical breeding selection of the offspring from carefully managed broodstock can lead to improved disease resistance and higher growth rates.