
Soy products replace fishmeal in offshore cobia feed study
A project of the Soy-in-Aquaculture program evaluated the feasibility of using soy protein concentrate and soybean meal to replace fishmeal in cobia diets.
The quality of postlarvae supplied by a shrimp hatchery can vary considerably. Common myths, such as acceptance of low survival and insufficient concern for water quality, can contribute to lower animal quality.

A project of the Soy-in-Aquaculture program evaluated the feasibility of using soy protein concentrate and soybean meal to replace fishmeal in cobia diets.

Research found that tobacco dust applied in culture water killed ramshorn snails within three days and did not compromise channel catfish.

A multinational project in Lombok, Indonesia, is focused on the identification and monitoring of improved seed collection and grow-out production methods for spiny lobsters.

In a study, the performance of gilthead sea bream juveniles fed diets with no fishmeal was compared to that of bream fed diets with 30 or 10 percent fishmeal.

Researchers studied the nature of muscle necrosis in shrimp by sampling infected shrimp from local ponds and challenging healthy specimen with filtrates from the diseased shrimp.

The 2001 detection of chloramphenicol in shrimp imported into the Netherlands heightened awareness of and anxiety over the presence of chemicals in food.

Those charged with determining the underlying cause of a disease outbreak have a wide variety of detective tools at their disposal.

Shrimp survival, weight, yield and feed conversion were better in farm units that operated with settling chambers for solids removal than in units without.

Combining biofloc technology with bio-secure modular shrimp culture can make operations more sustainable and economically viable. For optimized biofloc production, lined ponds and reservoirs and high stocking densities are essential. Paddlewheel aerators keep dissolved-oxygen levels high.

Germany produces a limited amount of carp, trout, mussels and other species. Although traditional pond-based farms continue to operate, the country’s aquaculture production is trending toward land-based systems that feature efficient resource use and reduced environmental impacts.

Male reproductive dysfunction has been increasingly reported in commercial shrimp maturation facilities. The authors recently carried out studies to characterize the reproductive capability of male black tiger shrimp.

One of the largest shrimp maturation operations in Ecuador is working with five major shrimp producers to improve growth rates.
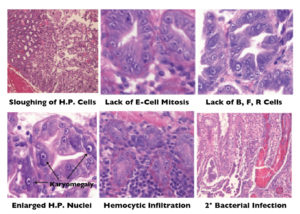
The emerging disease Early Mortality Syndrome has caused large losses among shrimp farmers. EMS is characterized by mass mortalities during the first 30 days of culture.

When aquaculture pond water suddenly warms, gas bubbles can form in the blood of aquatic animals and lead to stress or mortality.

In Peru, some wild cockle communities have been so overfished that total fishing bans are being considered. A project was therefore established to develop sustainable spat production as a crucial step toward the implementation of a conservation strategy for blood cockles that fosters social aquaculture and stock enhancement. The project rested on the establishment of protocols for reproduction, larval culture and seeding; development of diagnostic tools for molluscan pathogens and the study of blood cockles’ genetic diversity.