
Beneficial microbes and pathogen control
A range of alternative products is available to improve animal health and water quality, and control pathogen loads. Beneficial microbes produce antimicrobial compounds and suppress pathogen proliferation.
YY male tilapia technology, based on the genetic manipulation of sex, provides a robust, reliable method of achieving male fish. It avoids the use of hormones and maintains strain purity in genetically normal males.

A range of alternative products is available to improve animal health and water quality, and control pathogen loads. Beneficial microbes produce antimicrobial compounds and suppress pathogen proliferation.

The development of polymerase chain reaction testing to detect the bacteria that cause EMS is important, but confirmation by bioassay of presumptive positives to ensure pathogenicity is a prudent intermediate step.
1-monoglycerides are known for their antibacterial and antiviral effects in the human pharmaceutical and animal husbandry industries. As a substitution for the preventive use of antibiotics, these molecules are being evaluated in the fight against AHPND.

Highly controlled tank and raceway systems can help farmers raise postlarval shrimp to larger sizes before stocking in grow-out ponds. Raceways have recently been implemented for EMS management.

Research at the Oceanic Institute has been successful in overcoming bottlenecks associated with rearing small-mouthed fish larvae by finding a suitable first feed. Early work on the calanoid copepod Parvocalanus crassirostris focused on parameters necessary for successful maintenance of stock cultures.

In targeting grouper for new and sustainable farming technology, the authors developed an oral vaccine to control nervous necrosis virus (NNV) infection at the larval stage and multivalent injective bacterial and viral vaccines for the grow-out stage.

Shrimp-breeding programs release only a small fraction of their genetic material when they sell seed to clients for grow-out. This protects their large investment in developing the stocks so clients return for their next batch of seed instead of breeding the stocks themselves.

Iron compounds in fish contribute significantly to lipid oxidation in addition to oxidation mediated by enzymatic activity. The main iron-containing compounds are myoglobin and hemoglobin.

In a study, the authors evaluated the immune responses and host protection of hybrid catfish and channel catfish against the ich parasite (Ichthyophthirius multifiliis).

Hyper-intensive nursery systems for juvenile shrimp production present significant opportunities for shrimp farmers to increase profits. Nursery culture results in strong, healthy and uniform juveniles with great potential for compensatory growth when stocked in production ponds. Nurseries produce a maximum number of juveniles of a desired weight, and their use can reduce production costs by shortening time in growout ponds and increasing pond efficiency through additional cycles per year.

After experiencing disappointing survival rates following traditional artemia-based rearing protocols, the French hatchery Aquastream turned to a micropellet alternative to artemia.
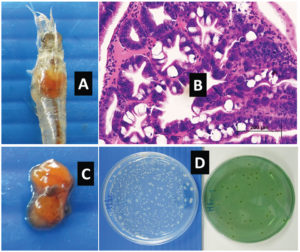
Monitoring of Vibrio bacteria in shrimp larvae determined a relationship among hepatopancreas color, bacteria concentration and signs of early mortality syndrome.

Although Bali is primarily a tourist destination, several small family-owned shrimp farms are located here. The Ndaru Luat Setio shrimp farm at Kubu raises specific pathogen-free Litopenaeus vannamei in ponds that apply basic biofloc technology with zero water exchange.

The introduction of tilapia to irrigation reservoirs in Israel improved the efficiency of water usage and reduced the cost of water needed for tilapia culture. Although requiring considerable investment, many dual-use reservoirs were constructed and equipped for efficient harvesting.

A trial in a lined, greenhouse-enclosed raceway evaluated the use of a heterotrophic biofloc system equipped with aeration, supplemental oxygen injection and centralized heating to achieve good shrimp production.