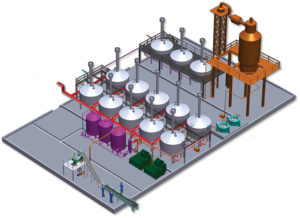
Broodstock center in India supports domestic shrimp-farming industry
The project produces specific-pathogen-free broodstock with good reproductive performance, fast growth and high survival. More than 60 hatcheries in India have received broodstock from the program.