Improving transportation of live hybrid striped bass
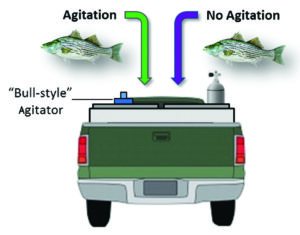
Anecdotal information has suggested that pond-reared hybrid striped bass are more vulnerable to transportation-related stressors than cage-reared fish. Study results suggested that accumulation of carbon dioxide and decreasing pH levels may contribute to this phenomenon. Agitation during simulated transport mitigated the carbon dioxide accumulation and stabilized pH, but shifted the total ammonia nitrogen equilibrium in favor of un-ionized ammonia nitrogen.Ultimately, the agitators did not substantially attenuate the stress responses observed in the fish.