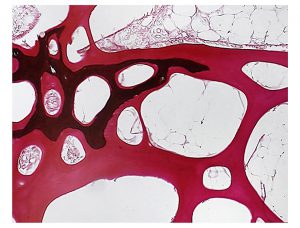
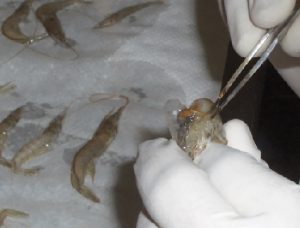
A holistic management approach to EMS
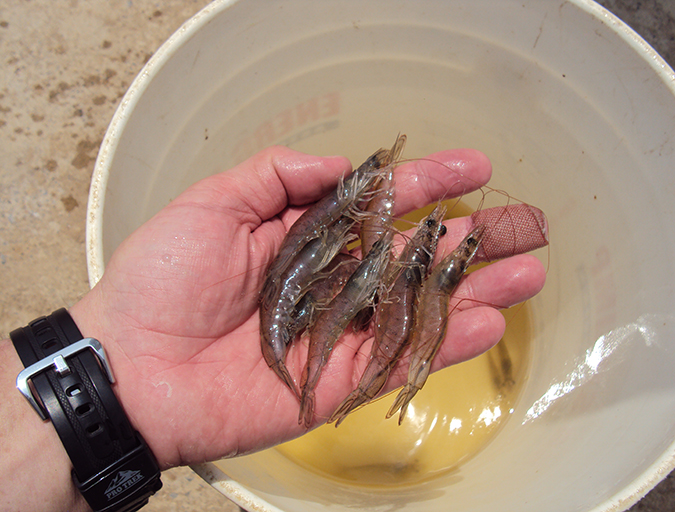
Early Mortality Syndrome has devastated farmed shrimp in Asia and Latin America. With better understanding of the pathogen and the development and improvement of novel strategies, shrimp farmers are now able to better manage the disease.