
New paradigms to help solve the global aquaculture disease crisis
Authors argue that interventions – like automated detection of pathogens and remote sensing applications – can help mitigate aquaculture's disease crisis.
Organic acids and autolyzed yeast products can reduce the impact of pathogens like microorganisms, viruses, parasites and fungi, supporting performance and profitability.

Authors argue that interventions – like automated detection of pathogens and remote sensing applications – can help mitigate aquaculture's disease crisis.

This study evaluated the growth performance of the freshwater fish piracanjuba raised in biofloc and clear-water systems for 34 days.

Study results indicate that P. vannamei challenged with AHPND in biofloc had higher survival rates than shrimp challenged in clear water.

This study evaluated through in vitro analyses the antimicrobial effectiveness of natural products used for P. vannamei bacterial diseases and antibiotics against pathogenic Vibrio strains circulating in Ecuadorian hatcheries.

The influence of antibiotics in fish and their effects on the gut microbiome aren’t well understood, says research team examining antimicrobial resistance.

As current antibiotics dwindle in effectiveness against multidrug-resistant pathogens, researchers are seeking potential replacements in some unlikely places.

Authors investigated the effects of replacing dietary fish oil with palm oil in juvenile Nile tilapia, and demonstrated that growth and feed utilization were not compromised when palm oil was used either partially or totally.

Study demonstrates strong association between White Feces Syndrome and Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei in EHP-endemic regions. Biosecurity strategies can minimize the risk of pathogen’s spread in the Americas.

This study in an outdoor biofloc technology production system evaluated impacts on fish production indices, common microbial off-flavors and water quality dynamics for hybrid tilapia.

This study evaluated the effect of feeding juvenile L. vannamei several times a day versus two and four times – manually or with an automatic feeder – with a low-fishmeal diet supplemented with crystalline amino acids.

This study investigated the effects of increasing levels of dietary soybean meal (SBM) with constant taurine supply in the induction of enteritis in juvenile totoaba.

The latest knowledge about fumonisins in aquaculture and the importance of preventing synergistic interactions between different mycotoxins.
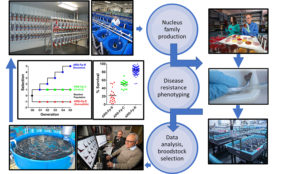
This study, involving more than 10 years of research on selective breeding, has shown that selective breeding can create considerable phenotypic divergence in rainbow trout lines when targeting a specific pathogen.

A research project aimed at improving shrimp hatcheries’ welfare practices shows there is a viable alternative to a common spawn-inducing technique.

Larviculture and culture density research with West Indian pointed venus is relevant to restocking efforts to support the extractive fisheries from natural banks and also for the development of aquaculture.