
Tiny Arctic crustacean improves larval and broodstock diets
A tiny Arctic crustacean can boost larval and broodstock nutrition as the organism is analogous to artemia in some respects.
Because of the natural feeding habits of the Brazilian fish pacu, it is relevant to evaluate the use of vegetable protein in their feed.

A tiny Arctic crustacean can boost larval and broodstock nutrition as the organism is analogous to artemia in some respects.

Traditionally, live foods such as diatoms and the brine shrimp artemia have been used in shrimp larviculture.

Clearly, there will be no single solution to our needs, but rather a combination of biotechnological and ecotechnological solutions.

Losses resulting from White Spot Syndrome Virus in Panama prompted new operational strategies to manage shrimp feeds.

To control costs with feed efficiency, it is desirable to minimize the protein percentage, but reductions should not compromise shrimp performance.

As marine-ingredient replacement with plant proteins continues, it's important to supplement diets with attractants to stimulate feeding behavior.

An alternative waste treatment is intense microbial processing of wastes to facilitate high yields with little or no water exchange.

A feeding trial evaluated five dietary protein sources on growth performance and phosphorus-retention efficiency in olive flounders.

Maintaining the stability of shrimp feeds until consumption is a challenge as pellets lose dry matter due to leaching of soluble compounds.

RAS inputs and outputs are easily quantified, but even an efficient system will appear to have higher operating costs than a traditional pond.

It is common practice to broadcast feed throughout a shrimp pond with a few feeding trays to help monitor consumption and adjust ration size.
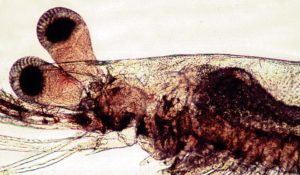
A report on the results of a study to determine the optimal dietary protein level for postlarvae Pacific white shrimp in a recirculating culture system.
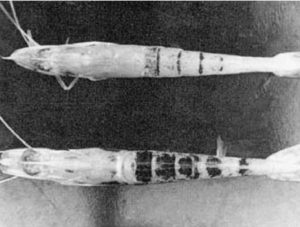
Dietary nutritional disorders in farmed aquatic animals can be broadly defined as diet-related imbalances due to “under-” or “over-” nutrition.
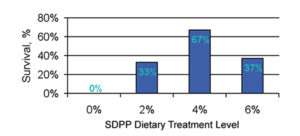
Spray-dried plasma protein is a high-protein feed ingredient that can lower occurrence of enteric disease when used in feed or water.

A variety of factors – postlarval nutrition, disease treatment and control of microflora – contribute to optimal hatchery operations.