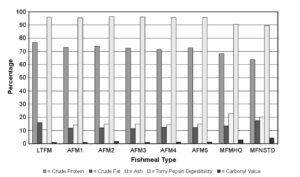
O.I. study confirms fishmeal quality in feed effects growth performance
The quality of fishmeal used as a dietary ingredient can influence the feed utilization and growth of the aquaculture species.
New ingredients and processes are figuring prominently in the production of more-nutritious and better-balanced “specialty" shrimp feeds.

The quality of fishmeal used as a dietary ingredient can influence the feed utilization and growth of the aquaculture species.

Ingredients are the major cost in the operation of a feed mill, so feasibility analyses should include real ingredient costs as well as manufacturing costs.

New feed practices can reduce environmental impacts of shrimp farming, including the replacement of fishmeal and fish oil with sustainable lipid sources.
Rendered meals, or feeds with ingredients made from animal byproducts, meet many important criteria and have excellent prospects for aquaculture feeds.

A water-soluble fraction of blue mussels improved the growth of juvenile Japanese flounders by increasing feeding.

Yellowtail snappers produce small larvae that are a challenge to rear. Initial protocols have resulted in survival of only 3 percent from egg to juvenile.

Evaluating trout performance fed diets with supplemental lysine in plant protein meal, and total ammonia nitrogen and soluble phosphorus excretion.
Soybean meal is increasingly being used in aquaculture feeds due to its nutritional quality and lower cost than animal protein sources.
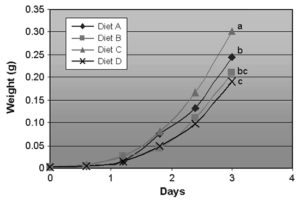
In a study at the University of Wales in the United Kingdom, a larval shrimp diet that included fresh marine ingredients was compared with a control diet.

Before shrimp farmers consider an on-site feed mill for aquafeed production, they should ask themselves tough questions and ponder all the risks.

CLA-enriched diets (with conjugated linoleic acid) have become a recent focus of fatty acid research because of their health benefits to humans.

Attractants are used in the aquafeed industry, where rapid identification and consumption of feed is very important in the aquatic environment.

Fishmeal and fish oil replacements present a challenge for the aquafeed industry. The range of alternative protein and fat sources is limited, given multiple considerations.

A feeding trial in Hawaii tested the nutritive value of extruded feeds in comparison pelleted feeds for Pacific white shrimp.

Diet microencapsulation using a biopolymer composite wall is a novel way to protect diet ingredients against deteriorative mechanisms such as oxidation and leaching.