
With byproducts, getting more from – and for – fish
Use of fish trimmings and byproducts in fishmeal and fish oil is a win for aquaculture. But challenges loom, including logistics and economics.
The third marine-ingredient-free feed contest launches today with an eye on carnivorous species, which face scrutiny for their dependence on fishmeal and fish oil.

Use of fish trimmings and byproducts in fishmeal and fish oil is a win for aquaculture. But challenges loom, including logistics and economics.

Findings of recent feeding trials with Siberian sturgeon and redfish demonstrate that mullet-based feeds can be substituted for traditional fishmeal resources.

The company has engaged in feed trials with both algae and microbial meals, before its sustainability director said farmers, “by and large, don’t want it.”

This study evaluated replacing fishmeal with a protein-rich and EPA-rich co-product of the marine microalga Nannochloropsis oculate in diets of Nile tilapia.

A commercial corn ethanol production byproduct (syrup) was used as a bacterial growth medium with the long-term aim to repurpose the resulting microbial biomass as a protein supplement in aquaculture feeds.

Qualitas Health, which grows algae in ponds in New Mexico and Texas for human supplements, is entering the alternative aquafeed ingredient market.

Fisheries improvements projects (FIPs) are an important mechanism for bettering South East Asian fisheries that supply into the aquafeed industry, a new report finds.

This study evaluated the effects of replacing fishmeal and fish oil with a plant-based diet in juvenile and on-growing rainbow trout from first-feeding.

How can the interesting and valuable research on alternate feed ingredients get from the laboratory bench to consumers’ bellies through market mechanisms?

Fish-free diets are suitable for shrimp production and can generate high-quality product. Consumer preferences for the flavor of shrimp and texture attributes need exploration.
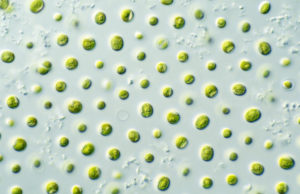
This study examined changes in the biochemical composition of the microalga Nannochloropsis sp. cultivated as a potential feedstock for aquafeeds, and presents results on its productivity, protein content and lipid composition.

A shift towards crop-based ingredients in shrimp feeds reduces dependency on marine resources but places resource demands onto the land and could impact the nutritional value of shrimp.

Functional ingredients and additives promote growth, improve health of farmed shrimp, and bolster immune response and other physiological needs.

At the F3 (fish-free feed) Companies Got Talent event in Burlingame, Calif., last week, alternative (non-marine) aquafeed ingredient companies spoke of decoupling aquaculture from fishmeal and fish oil in their quest for greater sustainability.
Massachusetts-based biotechnology firm KnipBio is the first single-cell protein manufacturer serving the aquafeed industry to earn Generally Regarded as Safe designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.