High-throughput genotyping tracks pedigrees, monitors diversity and assists with assignments to mating groups
Australia is one of the few shrimp-farming countries that will not introduce exotic shrimp species, including L. vannamei. Most Australian farmers produce black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon), although one farm has successfully produced banana shrimp (P. merguiensis) for several years. Traditionally, Australian farmers have relied on wild P. monodon broodstock, but over the past 10 years, substantial progress has been made in the domestication and selective breeding of Australian stocks of P. monodon.
Working with industry
In collaboration with the Australian companies Pacific Reef Fisheries, Australian Prawn Farms and Gold Coast Marine Aquaculture, and with support from the Queensland government, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) scientists are currently focusing on the development and implementation of technology to enable cost-effective, on-farm domestication and selective breeding of P. monodon. This includes screening of domesticated broodstock for endemic and exotic viruses, and the cost-effective application of genetic markers for tracking pedigrees and mate allocation.
Many of the major shrimp-breeding programs in the world rely on rearing separate families, artificial insemination and physical tagging. These techniques are not practical or cost-effective for the smaller-scale, on-farm breeding programs in Australia. Instead, the research collaboration between CSIRO and Australian industry partners is based on the use of high-throughput genotyping to track pedigrees, monitor diversity and assist with the assignment of individual males and females to pooled mating groups.
Increased performance
The three Australia companies have established on-farm founder stocks and are at different stages of development in their domestication and selective breeding of P. monodon. Gold Coast Marine Aquaculture (GCMA) has advanced the farthest to date.
Over the past four years, there has been a progressive increase in the performance of the domesticated and selectively bred GCMA stocks. In the 2008-2009 production season, the selected GCMA stocks yielded an average of 12.8 metric tons (MT) per hectare (ha), which was 50 percent greater than the average yields from adjacent ponds stocked at the same time with the progeny of wild broodstock.
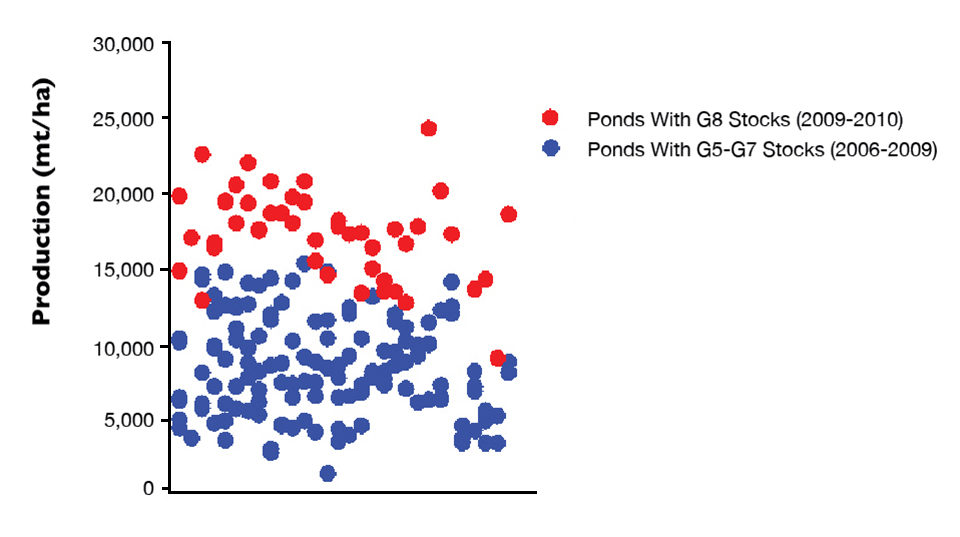
This production season, GCMA was the first Australian company to stock its entire farm with eighth-generation domesticated, selectively bred P. monodon. The performance of these stocks was outstanding, with an average yield for the whole farm of 17.5 metric MT/ha. Several ponds produced more than 20 mt/ha with a maximum in one pond of 24.2 MT/ha.
Comparison of the whole farm performance of these stocks with those of the previous three years, including ponds with domesticated stocks and ponds with wild stocks, demonstrates the enhanced performance of the eighth-generation stocks (Fig. 1).
Perspectives
The progressive improvement of the GCMA stocks has provided strong incentive for the other Australian farms to continue to develop their own P. monodon domestication and selective breeding programs. In parallel with the improvement in growth rates and survival, viral screening has revealed that the stocks have low loads of endogenous viruses. Furthermore, the improvements in yields have been achieved without compromising the market quality of the stocks. These are all vital factors for the long-term growth and prosperity of the Australian P. monodon-farming industry.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the September/October 2010 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Authors
-
Nigel Preston, Ph.D.
CSIRO Food Futures Flagship
233 Middle Street
Cleveland, Queensland 4163 Australia -
Greg Coman, Ph.D.
CSIRO Food Futures Flagship
233 Middle Street
Cleveland, Queensland 4163 Australia -
Jeff Cowley, Ph.D.
CSIRO Food Futures Flagship
233 Middle Street
Cleveland, Queensland 4163 Australia -
Nick Moore
Gold Coast Marine Aquaculture
Woongoolba, Queensland, Australia -
Brian Murphy
Gold Coast Marine Aquaculture
Woongoolba, Queensland, Australia
Tagged With
Related Posts

Health & Welfare
Brunei project develops technology for large black tiger shrimp production, part 1
A five-year project was undertaken in Brunei Darussalam to develop advanced technology for the production of large black tiger shrimp. A combination of technologies has enabled efficient production of large-sized black tiger shrimp, which could lead to a resurgence of this species in Asia.

Responsibility
A look at various intensive shrimp farming systems in Asia
The impact of diseases led some Asian shrimp farming countries to develop biofloc and recirculation aquaculture system (RAS) production technologies. Treating incoming water for culture operations and wastewater treatment are biosecurity measures for disease prevention and control.

Innovation & Investment
Artemia, the ‘magic powder’ fueling a multi-billion-dollar industry
Artemia, microscopic brine shrimp used as feed in hatcheries, are the unsung heroes of aquaculture. Experts say artemia is still inspiring innovation more than 50 years after initial commercialization. These creatures are much more than Sea-Monkeys.

Health & Welfare
EHP a risk factor for other shrimp diseases
Laboratory challenges and a case-control study were used to determine the effects of EHP infection on two Vibrio diseases: acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease (AHPND) and septic hepatopancreatic necrosis (SHPN).



