Gold Coast Marine Aquaculture and Genics develop a commercial solution to a daunting disease challenge

With the recent occurrence of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in New South Wales, Australia, Gold Coast Marine Aquaculture (GCMA) is showing how to profitably grow black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) in the presence of the disease.
In late 2016, WSSV devastated the Southeast Queensland black tiger shrimp industry situated in the Logan River region. Imported, WSSV-infected, raw uncooked shrimp – intended for human consumption but used as bait by recreational fishermen – are thought to be the vector for the pathogen.
A biosecurity control zone was established and all shrimp farming operations in the zone eliminated their animals under government orders. Unfortunately, this included animals from one of the world’s most successful P. monodon breeding programs at GCMA.
A movement restriction area was then established that extends from Caloundra in Queensland to the New South Wales border and west to Ipswich in Queensland, which means the movement of potential carriers within and out of this area is prohibited.
All P. monodon farming operations within the MRA were halted for two years during which time they each prepared strategies to mitigate the potential threat from WSSV when operations could resume. While the region only realized one successful season without WSSV on farms, there was one particular strategy that has lasted the test of time and proven successful for multiple seasons which is that of GCMA, explains Dr. Melony Sellars of Genics Pty Ltd.
Can this breeding technique breathe new life into giant freshwater prawn farming?
“A key challenge of WSSV is that it is carried as a subclinical infection in a wide [variety] of host animal species without showing clinical signs of disease. Disease onset is determined by environmental or other stressors, such as temperature variations and handling, which leads to an acute event with rapid mortalities in susceptible species such as Penaeid shrimp,” said Dr. Sellars. “Furthermore, there is no easy fast-acting treatment for WSSV, making prevention and/or breeding for tolerance/resistance the best strategy to mitigate risk.”

Dr. Sellars said it is now accepted that WSSV is ever present in the Logan River ecosystem, both in wild shrimp species and other species of decapod crustaceans, making appropriate treatment and management of water coming onto the farms of upmost importance.
GCMA tested several strategies for suitable water treatment to eliminate WSSV and ultimately designed a solution that has been working since 2019 to keep WSSV out of its farm.
Water is treated at time of pumping from the Logan River with a commercial biocide and then at the farm site filtered by drum filters down to 50 micrometers (µm, one-millionth of a meter), before going to settlement (Fig. 1). The biocide is only used for pond filling, not for subsequent water exchanges during production where the drum filters are used for removing potential vectors.
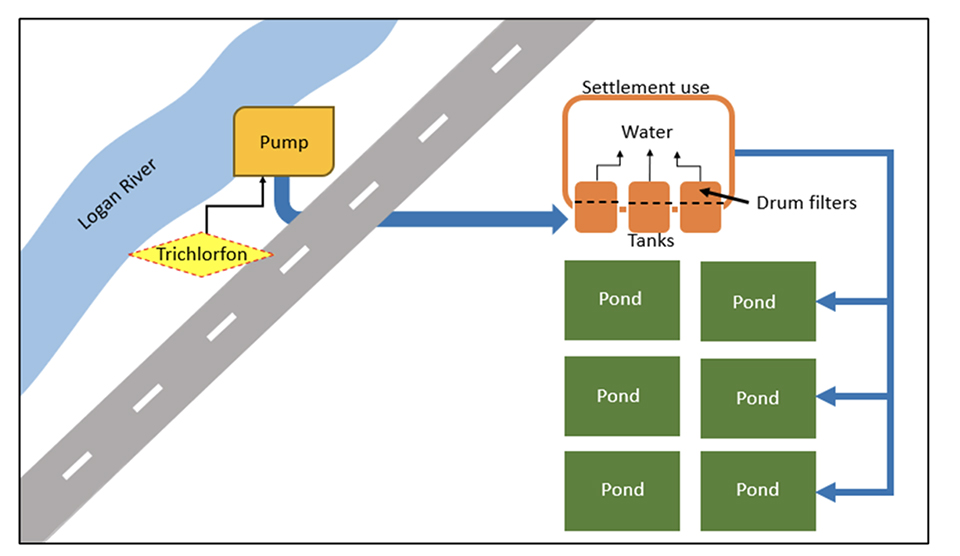
The biocide is added at a concentration of 0.5 parts per million (0.5 milligrams per liter) 50 percent active ingredient at the pumping site. Next in line are the OHEX German-made 50-µm drum filters. A distance of 20 to 30 meters separates each section, having the biocide already acting before mechanical filtration, therefore cleaning the water even before arriving at the filters. A 10- to 12-day withholding period follows before going to the ponds and having shrimp stocked.
Dr. Sellars said she hopes this real-world commercial story of successfully growing shrimp in the presence of WSSV is a testament to the resilience of shrimp producers over the world and an example for other regions to follow.
Follow the Advocate on Twitter @GSA_Advocate
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Author
Tagged With
Related Posts

Responsibility
Crouching Tigers: Bangladesh shrimp farming at a critical juncture
With improver programs and branding opportunities for its black tiger producers, Bangladesh shrimp farming eyes a more profitable future.

Health & Welfare
Australian research partnership maps the black tiger prawn genome
A collaboration of research institutes and industry has mapped the genome of an iconic Australian seafood species, the black tiger prawn.

Intelligence
Assessing the effects of low pH on taste, amino acid composition of black tiger shrimp
The effect of low pH on the survival and amino acid composition of shrimp suggests ocean acidification may affect future quality, quantity.

Intelligence
Bangladesh seeks more buck for its ‘bagda’
As more than 80 percent of Bangladeshi shrimp exports already go to EU markets, a consultation meeting involving buyers from the bloc and Bangladesh industry stakeholders and authorities was held at the end of last month in Utrecht, the Netherlands.



