Study evaluates water absorption and percentage loss of dry matter due to leaching
The use of binder agents in feeds to increase their stability in water can affect feed consumption. It is important to ensure good feed ingestion rates to obtain maximum growth, while minimizing nutrient leaching.
The authors recently conducted a study at the Mariculture Program of the Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León in Mexico to determine if the consumption of steam-pelleted feeds was affected by the use of different natural or synthetic binder agents.
Feed study
The feeds were manufactured at a commercial feed manufacturing plant in Ecuador using standard steam-pelleting techniques. Formulation of all diets was identical except for the nature and inclusion rate of the binders, which were added in substitution for part of the wheat middlings (Table 1).
Cerecer-Cota, Composition of the experimental feeds, Table 1
| Ingredient | Wheat Gluten 0.3 | Synthetic Binder 0.6 | Kelp Meal 3.5 | No Binder |
|---|
Ingredient | Wheat Gluten 0.3 | Synthetic Binder 0.6 | Kelp Meal 3.5 | No Binder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Whole wheat meal | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Fishmeal | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Wheat middlings | 19.7 | 19.4 | 16.5 | 20 |
| Rice polishings | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Feather meal | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Fish oil | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Soybean meal | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Vitamin and mineral mix | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 |
| Soy lecithin | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
A feeding trial was carried out over a 28-day period with juvenile Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Four replicate tanks containing 10 animals each were used for each feed. The shrimp were fed twice daily using feed trays. Feed consumption was evaluated using a quantitative method in which the dry weight of consumed feed was corrected by subtracting the loss of dry matter estimated after a one-hour immersion of the pellets in sea water.
Pellet physical characteristics
Pellet water absorption and the percentage loss of dry matter due to leaching were determined using standard techniques. The hardness of both dry and wet pellets was analyzed with a texturometer using a method developed in collaboration with researchers at the University of Sonora, Mexico. Hardness was expressed as the maximum force needed to cause a given deformation.
Diet/consumption correlations
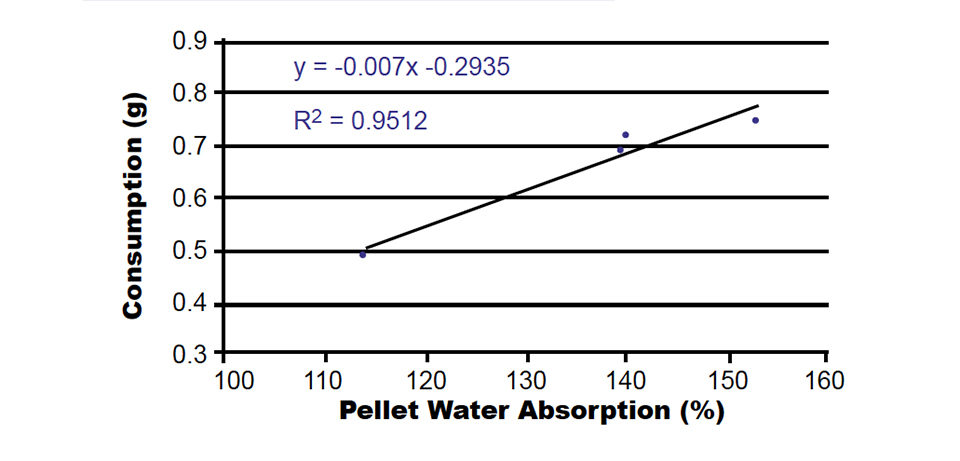
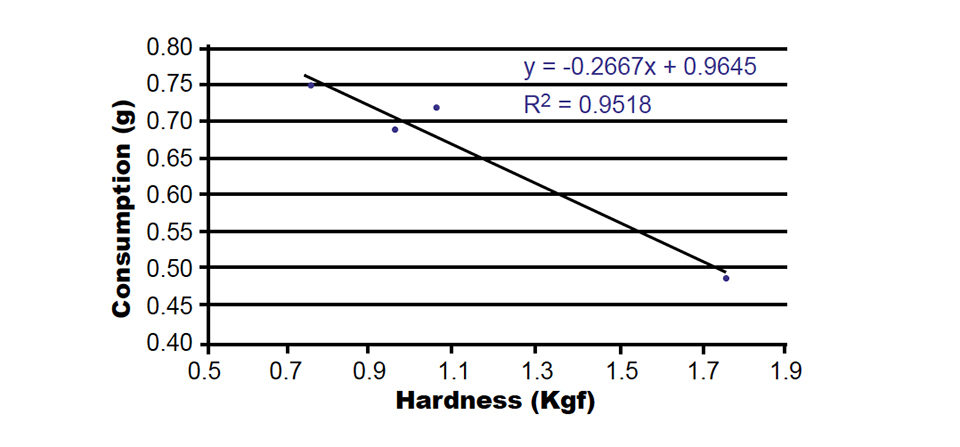
The addition of different binder agents to the feeds changed the capacity of the feeds to absorb water as well as feed consumption by shrimp (Table 2). An inverse relationship was found between water absorption and pellet hardness.
Cerecer-Cota, Physical properties and consumption, Table 2
| Property | Wheat Gluten 3.0 | Synthetic Binder 0.6 | Kelp Meal 3.5 | No Binder |
|---|
Property | Wheat Gluten 3.0 | Synthetic Binder 0.6 | Kelp Meal 3.5 | No Binder |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water absorption (%, after 60 minutes) | 140 ± 3b | 114 ± 1a | 139 ± 1b | 153 ± 16b |
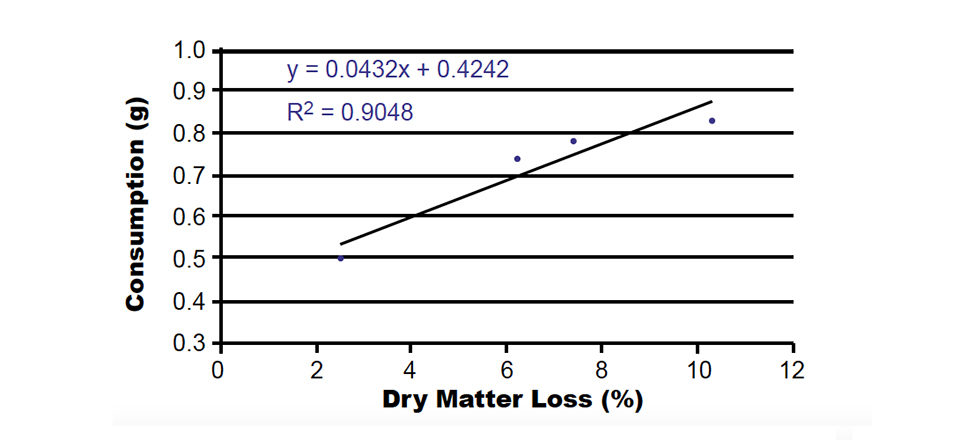
| Dry matter loss (%, after 60 minutes in water) | 7.5 ± 0.4c | 2.6 ± 0.2a | 6.3 ± 0.2b | 10.4 ± 0.3d |
| Wet pellet hardness (Kgf, after 60 minutes in water) | 1.06 ± 0.11b | 1.75 ± 0.17c | 0.96 ± 0.20ab | 0.76 ± 0.05a |
| Dry pellet hardness (Kgf) | 106 ± 10b | 88 ± 4a | 96 ± 8a | 90 ± 6a |
| Individual consumption (g dry matter) | 0.78 ± 0.12a | 0.50 ± 0.18b | 0.74 ± 0.12a | 0.83 ± 0.04a |
| Individual consumption (g dry matter, corrected) | 0.72 ± 0.11a | 0.49 ± 0.18b | 0.69 ± 0.11a | 0.75 ± 0.03a |
The control feeds, manufactured without a binder agent, had the best water absorption capacity and highest loss of dry matter, but were the most consumed feeds. The feeds containing synthetic urea-formaldehyde as a binder agent were the hardest after being immersed in sea water, but also the least consumed.
When feed consumption was correlated with the physical parameters, high correlation coefficients were found (Figs. 1-3). Wet pellet hardness was inversely correlated with consumption.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the April 2005 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Authors
-
Estrella E. Cerecer-Cota
Programa Maricultura
Fac. Ciencias Biológicas
Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León
Cd Universitaria, A.P. F-56
San Nicolás de los Garza
Nuevo León 66450, México -
Denis Ricque-Marie, Ph.D.
Programa Maricultura
Fac. Ciencias Biológicas
Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León
Cd Universitaria, A.P. F-56
San Nicolás de los Garza
Nuevo León 66450, México -
Fernando Mendoza-Cano
Programa Maricultura
Fac. Ciencias Biológicas
Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León
Cd Universitaria, A.P. F-56
San Nicolás de los Garza
Nuevo León 66450, México -
Martha G. Nieto-López, Ph.D.
Programa Maricultura
Fac. Ciencias Biológicas
Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León
Cd Universitaria, A.P. F-56
San Nicolás de los Garza
Nuevo León 66450, México -
L. Elizabeth Cruz-Suárez, Ph.D.
Programa Maricultura
Fac. Ciencias Biológicas
Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León
Cd Universitaria, A.P. F-56
San Nicolás de los Garza
Nuevo León 66450, México -
Benjamín Ramírez-Wong, Ph.D.
Universidad de Sonora
Hermosillo, México -
M. Guadalupe Salazar-García, Ph.D.
Universidad de Sonora
Hermosillo, México -
Mario Velasco-Escudero, Ph.D.
Marnetec S.L.
Barcelona, Spain
Tagged With
Related Posts

Aquafeeds
A look at protease enzymes in crustacean nutrition
Food digestion involves digestive enzymes to break down polymeric macromolecules and facilitate nutrient absorption. Enzyme supplementation in aquafeeds is a major alternative to improve feed quality and nutrient digestibility, gut health, compensate digestive enzymes when needed, and may also improve immune responses.

Aquafeeds
A look at the SME controlled extrusion process
A study was conducted using a Twin-Screw Extruder equipped with Specific Mechanical Energy (SME) and Density Control valves, to determine the effect of SME on the water stability of shrimp feeds. Further research is needed to evaluate the performance.

Aquafeeds
Analyzing the hydrostability of shrimp feeds
The physical integrity and nutrient leaching of shrimp aquafeeds are important aspects in their quality control. The water stability of shrimp aquafeeds is often evaluated in various subjective manners. This analytical procedure provides a baseline for the aquafeed manufacturer to assess product quality.

Aquafeeds
Aquaculture feed composition helps define potential for water pollution
A study found that feed for salmon and trout had higher organic carbon concentrations than did catfish, shrimp and tilapia feeds. Nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations were similar among salmon, trout and shrimp feeds, and higher than those in catfish and tilapia feeds.


