Requirements for plant ingredients in aquafeeds similar to those for swine, poultry

Land use is an important issue in assessing environmental stewardship by aquaculture projects. Aquaculture is becoming more intensive, and the space requirements for culturing aquatic animals are decreasing. Nevertheless, space used directly for culture is only one of the space requirements for aquaculture.
In pond culture, land is used for embankments, canals, and other earthwork. Aquaculture facilities also must have access, storage, and staging areas. Moreover, agricultural land must be dedicated to producing plant materials used in aquaculture feed. The fishmeal and fish oil in feed must be made from marine fish, which requires additional space.
Plant-based feed ingredients
Corn meal, soybean meal, peanut meal, cottonseed meal, wheat middlings, rice flour and vegetable oils are common plant products used in aquaculture. Cottonseed meal and wheat middlings are by-products of cotton fiber and wheat flour production. Vegetable oils are extracted from soybeans and peanuts in the process of making meals.
Thus, there are no land requirements for cottonseed meal, wheat middlings and vegetable oils, because the use of these products in aquaculture feeds does not require land dedicated specifically for their production. However, land must be dedicated to the production of the corn, soybean, and peanut meals used in feed.
About 40 percent of the marine fishmeal production and 80 percent of the marine fish oil production are used in aquaculture feeds. Fishmeal is a primary product produced specifically for aquaculture feed, but fish oil is a byproduct of fishmeal production. Shrimp head meal and animal meat meals are other by-products used in aquaculture feeds.
Land requirements
As defined by United States Department of Agriculture statistics, land requirements for the production of corn, soybean, and peanut meals are shown in Table 1. About 4.5 metric tons (MT) of live fish are used to make 1 MT of marine fishmeal. However, calculations of the ocean area necessary to produce fishmeal will not be addressed here.
Boyd, Average age of plant meals, Table 1
| Product | Seed Yield (kg/ha) | Meal Yield (kg/ha) |
|---|
Product | Seed Yield (kg/ha) | Meal Yield (kg/ha) |
|---|---|---|
| Corn meal | 9,413 | 9,413 |
| Soybean meal | 2,824 | 2,231 |
| Peanut meal | 3,440 | 1,927 |
Typical feed ingredients and feed-conversion ratios (FCRs) obtained from scientific literature for salmon, trout, shrimp, tilapia, and channel catfish feeds are provided in Table 2. For these feeds, the only ingredients considered specifically produced for aquaculture are fishmeal and corn and soybean meals.
Boyd, Breakdown of major ingredients, Table 2
| Salmon | Ingredient Content (%) Atlantic Trout | Ingredient Content (%) Trout | Ingredient Content (%) Shrimp | Ingredient Content (%) Tilapia | Ingredient Content (%) Channel Catfish |
|---|
Salmon | Ingredient Content (%) Atlantic Trout | Ingredient Content (%) Trout | Ingredient Content (%) Shrimp | Ingredient Content (%) Tilapia | Ingredient Content (%) Channel Catfish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean meal | 14.0 | 15.0 | 24.5 | 38.3 | 34.5 |
| Cottonseed meal | – | – | – | 50.8 | 12.0 |
| Corn meal | 10.0 | – | – | – | 22.4 |
| Wheat middlings | 18.0 | 27.0 | 27.5 | 4.0 | 20.0 |
| Fishmeal | 30.0 | 25.0 | 19.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| Shrimp head meal | – | – | 13.5 | – | – |
| Squid meal | – | – | 5.0 | – | – |
| Rendered products | – | 15.0 | – | – | 4.0 |
| Oil | 24.0 | 16.0 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| Feed-conversion oil | 1.0 | 1.2 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 2.2 |
The land area necessary to provide plant meals for enough feed to produce 1 MT of live tilapia is calculated below using the following equation:
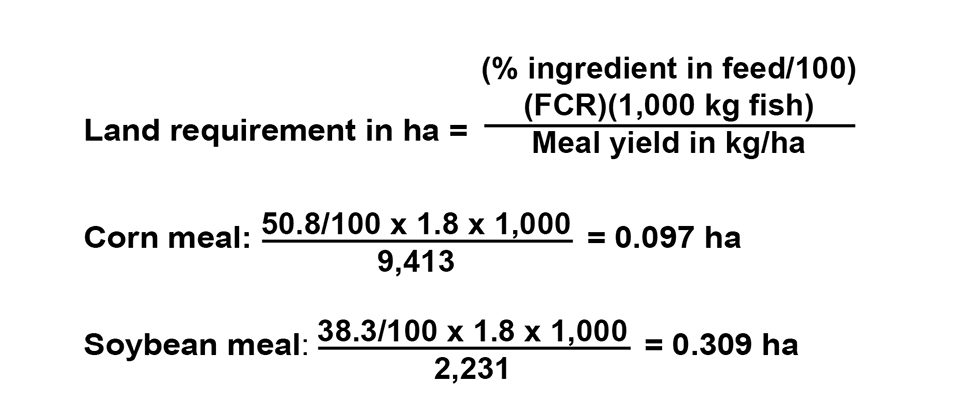
The total area needed for producing plant meals is 0.097 + 0.309 ha, or 0.406 hectare per metric tons tilapia.
The tilapia feed also contained 4 percent fishmeal. At a feed conversion of 1.8, 72 kg of fishmeal would be needed to produce 1,000 kg of tilapia. At a conversion of 4.5 kg live fish per kilogram fishmeal, 324 kg of marine fish would be used in feed to produce 1,000 kg of tilapia.
The land requirements for plant ingredients and quantity of marine fish for fishmeal for the production of five fish species are given in Table 3. The culture of 1 MT of salmon or trout requires less than 0.1 ha of land area for plant ingredients, while 1 MT of catfish or tilapia takes about 0.4 ha of land for plant-based feed ingredients. For shrimp, about 0.2 ha of land is required to produce plant ingredients for feed to produce 1 MT. The live fish requirements for fishmeal are much higher in feeds for salmon, trout, and shrimp than those for catfish and tilapia.
Boyd, Land area and live marine fish volume needed for feed ingredients to produce 1 mt, Table 3
| Salmon | Land Area (ha) Atlantic Shrimp | Land Area (ha) Trout | Land Area (ha) Shrimp | Land Area (ha) Tilapia | Land Area (ha) Channel Catfish |
|---|
Salmon | Land Area (ha) Atlantic Shrimp | Land Area (ha) Trout | Land Area (ha) Shrimp | Land Area (ha) Tilapia | Land Area (ha) Channel Catfish |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean meal | 0.063 | 0.081 | 0.220 | 0.309 | 0.340 |
| Corn meal | 0.011 | – | – | 0.097 | 0.052 |
| Fish (kg) | 1,350 | 1,350 | 1,710 | 324 | 396 |
Comparing space requirements
It is interesting to compare the space requirements for plant meals used in aquatic animal and terrestrial animal production. A typical feed for swine contains 74.4 percent corn and 23.4 percent soybean meal, while broiler feed is 67.0 percent corn and 23.7 percent soybean meal. Feed-conversion ratios are about 2.8 for swine and 1.88 for broilers. The land requirements for plant ingredients in feed for 1 MT net production are 0.515 and 0.333 ha for swine and broilers, respectively. The land requirements for plant ingredients in feeds for catfish and tilapia are similar to those for swine and poultry. Fishmeal and fish oil are not used in typical swine and broiler feeds.
Total land area requirements
Studies could determine the usual ratio of the total area of an aquaculture facility to the water surface area of its production units. Preliminary results from a study of channel catfish farming suggested the ratio may be about 1.25:1. Production often reaches 8 metric tons per hectare per year in channel catfish farming, but the total land area used to grow 8 MT of catfish is more than 1 ha.
About 0.25 ha is necessary for direct support of the production facility. Another 3.14 ha are needed to produce the plant meals used in feed. Thus, the production of 8 mt of channel catfish requires 4.39 ha of land. It also could be said that it takes 3.39 ha of land to support 1 ha of channel catfish culture in ponds. In addition, if the feed contains 4 percent fishmeal, 3.14 MT of live marine fish would be needed to produce fishmeal for the feed.
Fish often are cultured at high density in raceways and cages. For example, high-density cages for tilapia culture can yield 100 kg fish per cubic meter. Some large tilapia farms produce up to 10,000 MT of tilapia annually in cages covering about 1 ha of water surface area. About 4,000 ha of land will be devoted to producing plant meal for use in the feed for such a farm. At a fishmeal content of 4 percent, about 3,240 MT of marine fish would be necessary to make fishmeal for 10,000 MT of tilapia. The space requirement per mt of production is small in raceways and cages, and almost all of the land use is for producing feed ingredients.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the April/May 2006 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Author
-

Claude E. Boyd, Ph.D.
Department of Fisheries and Allied Aquacultures
Auburn University
Alabama 36849 USA
Tagged With
Related Posts

Intelligence
A brief look at genetically modified salmon
If approved by FDA, fast-growing genetically modified salmon will provide a safe and nutritious product similar to other farmed Atlantic salmon.

Health & Welfare
A case for better shrimp nutrition
Shrimp farm performance can often be below realistic production standards. Use proven nutrition, feeds and feeding techniques to improve profitability.

Health & Welfare
A holistic management approach to EMS
Early Mortality Syndrome has devastated farmed shrimp in Asia and Latin America. With better understanding of the pathogen and the development and improvement of novel strategies, shrimp farmers are now able to better manage the disease.

Aquafeeds
A look at India’s fish feed industry
India's fish-farming industry makes limited use of modern feeds, providing potential for the feed sector to grow. Commercial feeds are predominantly used for pangasius farming, followed by a rising popularity in carp culture.

