Look at 28 nutrition studies shows limited possibilities for fishmeal substitution

Growth in aquaculture, especially of carnivorous species in Europe, has caused increasing pressure on markets for marine raw materials. The availability of fishmeal for aquafeed has become a concern because the market for fishmeal is a global one. The swine and poultry industries consume over half of the global fishmeal production, although their reliance on fishmeal is not as rigid as that of aquaculture because alternative feeds are more substitutable in those sectors.
Aquaculture’s share of the fishmeal market has risen sharply over the past several years, and projections show this share will continue to increase as aquaculture grows further. Since fishmeal and oil production have probably reached their production limits, increased demand from aquaculture can only be met through diversion of inputs from other sources or substitution with suitable replacements.
The authors recently conducted a study to explore the potential for and implications of increased substitution of alternative feeds for fishmeal in diets for salmon and trout. In this study, meta-analysis was used to synthesize the results of empirical studies.
Meta-analysis of data
While individual studies have looked at the effects of different food combinations on fish growth, each study examined only a limited range of alternatives. However, across the studies, a wide range of combinations can be considered.
In a meta-analysis of earlier research, the authors examined 16 studies that concerned the substitution or replacement of fishmeal in diets for trout and 12 studies for salmon. Each study considered several alternative feed regimes, resulting in a total of 77 feed combinations for trout and 49 for salmon.
This research was an assessment of the influences of dietary characteristics on potential substitutability, compared to system influences of study methodology or experimental design. This information can provide insight into the overall substitutability of fishmeal with vegetable proteins and provide a diet composition that achieves the highest growth with minimal effects on economic performance.
Results
Results of the authors’ work, which was based on the Morishima Elasticity of Substitution values, indicated there was substitutability between ingredients for salmon and trout feeds (Table 1). Full details were explained in an article by the authors in the proceedings of the 2005 European Association of Agricultural Economists, 95th Seminar, in Rome, Italy.
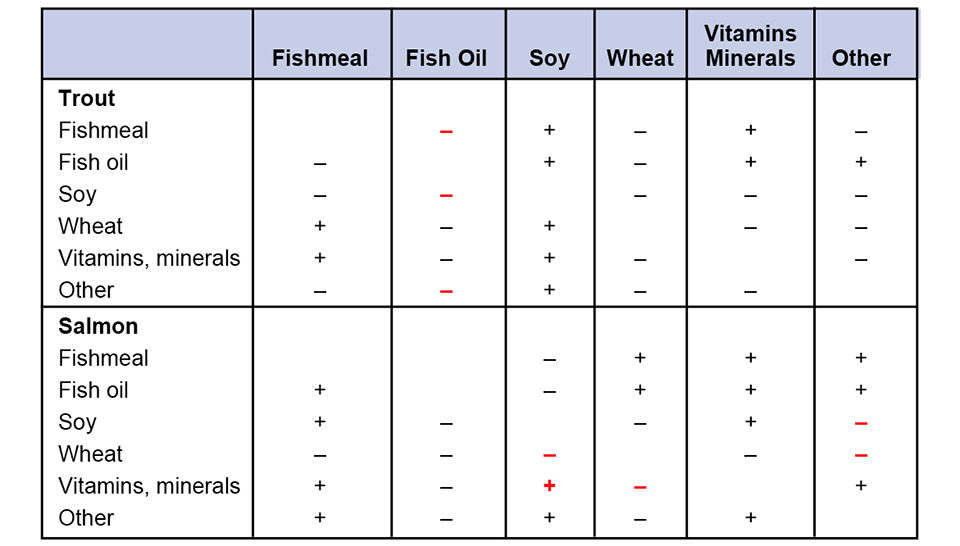
In diets for trout, it was found that soy meal and other ingredients that made up the protein content of the diets could substitute for fish oil while maintaining current levels of productivity. Although, as expected, many of the elasticity measures showed some degree of substitutability between ingredients, the values were largely not significant for both salmon and trout, although more substitution possibilities between ingredients were noted for salmon. For example, soy meal can substitute for wheat and combinations of other ingredients can replace soy meal and wheat while maintaining productivity.
In addition, for trout, experimental design had little effect on growth, indicating that only feed contributed to growth and further highlighting the importance of fishmeal. However, for salmon, experimental design was a significant factor in affecting the ways in which the fish grew. A number of alternative ingredients were also found to have a relationship, indicating that if productivity is to be maintained, such complementary ingredients must be increased.
Cost effectiveness

Based on the meta-analysis production model, the cost effectiveness of alternative feeds for salmon was examined using a stochastic simulation approach. That is, the growth implications and costs of alternative combinations of feed were examined using random combinations of feeds.
The costs for combinations of feeds that produced at least equivalent growth rates over equivalent times were examined. Full details of the analysis and results were presented by the authors in the 2006 Proceedings of the 13th Biennial Conference of the International Institute of Fisheries Economics and Trade.
The simulation results found that a number of feed combinations, excluding fish-based feeds, could be used to produce similar output at lower cost than the current feed combinations. When replacing fishmeal in diets for salmon, all other ingredients in the diet needed to be increased. Soy, wheat, and “other” cereals were all increased by a factor of approximately three. In addition, the inclusion of vitamins and minerals was increased by a factor of two.
(Editor’s Note: This article was originally published in the March/April 2007 print edition of the Global Aquaculture Advocate.)
Now that you've reached the end of the article ...
… please consider supporting GSA’s mission to advance responsible seafood practices through education, advocacy and third-party assurances. The Advocate aims to document the evolution of responsible seafood practices and share the expansive knowledge of our vast network of contributors.
By becoming a Global Seafood Alliance member, you’re ensuring that all of the pre-competitive work we do through member benefits, resources and events can continue. Individual membership costs just $50 a year.
Not a GSA member? Join us.
Authors
-
Ben Drakeford
Centre for the Economics and Management of Aquatic Resources
University of Portsmouth
Burnaby Terrace, 1-8 Burnaby Road
Portsmouth PO1 3AE United Kingdom -
Sean Pascoe
CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research
Cleveland, Australia
Tagged With
Related Posts

Aquafeeds
Alternatives to fishmeal perform well in low-salinity shrimp farm trial
In a white shrimp farm trial in a low-salinity environment, alternatives to fishmeal did not negatively impact the growth, survival or FCR of the shrimp.

Aquafeeds
A look at corn distillers dried grains with solubles
Corn distillers dried grains with solubles are an economical source of energy, protein and digestible phosphorus to reduce feed costs and fishmeal usage.

Aquafeeds
A look at protease enzymes in crustacean nutrition
Food digestion involves digestive enzymes to break down polymeric macromolecules and facilitate nutrient absorption. Enzyme supplementation in aquafeeds is a major alternative to improve feed quality and nutrient digestibility, gut health, compensate digestive enzymes when needed, and may also improve immune responses.

Aquafeeds
A new nutrient for aquaculture, from microbes that consume carbon waste
Biotechnology firm NovoNutrients aims to produce a line of nutraceutical aquafeed additives as well as a bulk feed ingredient that can supplement fishmeal. Its process includes feeding carbon dioxide from industrial gas to a “microbial consortium” starring hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria.


